Fig. 3.
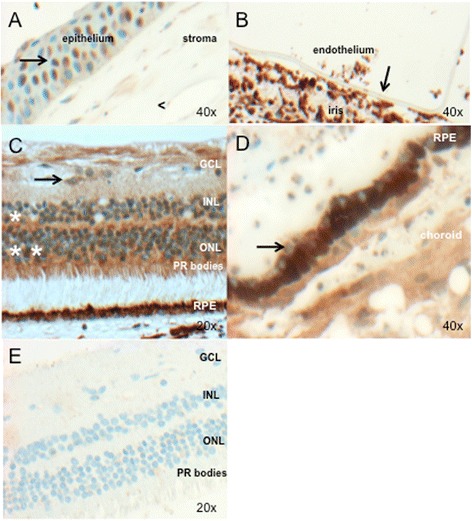
PRDM5 expression in the adult human eye (a–d) (control #2, Table 1). Image objective magnifications (OM) are shown. PRDM5 staining is brown (obtained using DAB as the chromogen). a. Nuclei of the corneal epithelium are positive for PRDM5 (arrow). The corneal stroma shows mild cytoplasmic staining, but nuclei are negative (<). b. PRDM5 is not expressed in the corneal endothelium (arrow) (in this image the endothelium has become detached from the overlying stroma). c. Positive PRDM5 nuclear and cytoplasmic staining in the inner (*) and outer nuclear layers (**), with cones staining more strongly than rods. Ganglion cell cytoplasm are also positive (arrow). Ocular tissue from patient P1 with deletion exons 9–14 is shown in (e). GCL, ganglion cell layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer; PR, photoreceptors, RPE; retinal pigment epithelium. d. Retinal pigment epithelium cell nuclei (arrow) appear negative. e. PRDM5 staining in P1 with PRDM5 deletion exons 9–14, demonstrating loss of PRDM5 nuclear and most cytoplasmic staining in the retina associated with loss of antibody epitope
