Fig. 5.
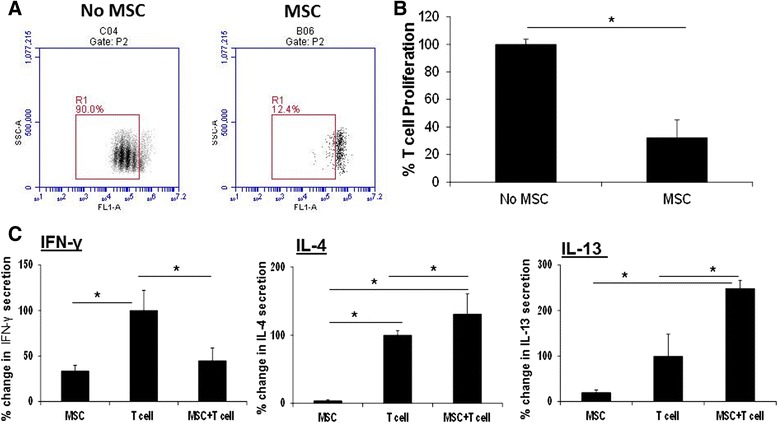
L-MSCs suppress mitogen-stimulated T-cell proliferation and Th1 cytokine secretion and promote Th2 cytokine secretion by T cells. a L-MSCs inhibit mitogen-stimulated T-cell proliferation. L-MSCs (1 × 105/well) were plated in a 24-well plate overnight. CFSE-labeled PBMCs (1 × 106/well) isolated from unrelated pigs were added to L-MSC cultures and stimulated with PHA (5 μg/ml). L-MSC–PBMC co-cultures were incubated for 72 h at 37 °C. The cell proliferation was analyzed by flow cytometry. A representative flow diagram is shown. b Data are presented as % change in proliferating T cells relative to PHA-stimulated PBMCs without MSC group (PBMCs stimulated with PHA were considered as 100 %). The experiment was performed with L-MSCs/PBMCs isolated from three different pig pairs. * P < 0.05, versus the no MSC group. c L-MSCs inhibit Th1 and enhance Th2 cytokine production by T cells. PBMCs were stimulated with PHA in the presence or absence of L-MSCs for 24 h. After the incubation, the supernatants were collected and examined for Th1 (IFN-γ) and Th2 (IL-4 and IL-13) cytokine production by ELISA. Data are expressed as % change in IFN-γ, IL-4 and IL-13 production in L-MSC/PBMC co-cultures relative to PHA-stimulated PBMCs (PBMCs stimulated with PHA considered as 100 %). The values are means ± SD. *P < 0.05. The experiments were performed with L-MSCs and PBMCs isolated from three germ-free and SPF pigs respectively. IFN Interferon, IL Interleukin, MSC Mesenchymal stem cell
