Fig. 3.
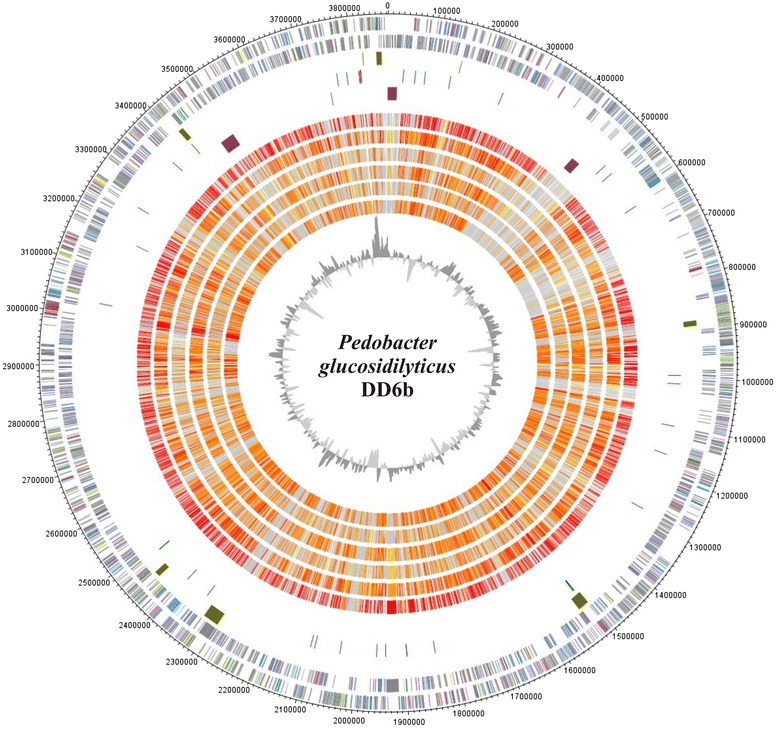
Genome comparison of P. glucosidilyticus DD6b with 6 completely genome-sequenced Pedobacter type strains: Genes encoded by the leading and the lagging strand (circle 1 and 2) of P. glucosidilyticus DD6b are marked in COG colors in the artificial chromosome map. Visualization was done with DNAPlotter [46]. Genomic islands (olive) identified with IslandViewer [47] are shown in circle 3, tRNAs (green) and rRNAs (pink) in circle 4. Special features of strain DD6b are marked in purple in circle 5 and described in the plain text. The presence of orthologs (circle 6 to 11) is indicated for the genomes of P. glucosidilyticus, DSM 23,534 (AULF00000000), P. borealis DSM 19,626 (JAUG00000000), P. heparinus HIM 762–3, DSM 2366 (CP001681.1), P. agri PB92 (AJLG00000000), P. oryzae DSM 19,973 (AUHA00000000) are illustrated in red to light yellow and singletons in grey (grey: >e−10-1; light yellow: <e−50- > e−10; gold: <e−50- > e−90; light orange: <e−90- > e−100; orange: <e−100- > e−120; red: <e−120-0). The innermost plot represents the GC-content. Paralogous genes were excluded from this analysis
