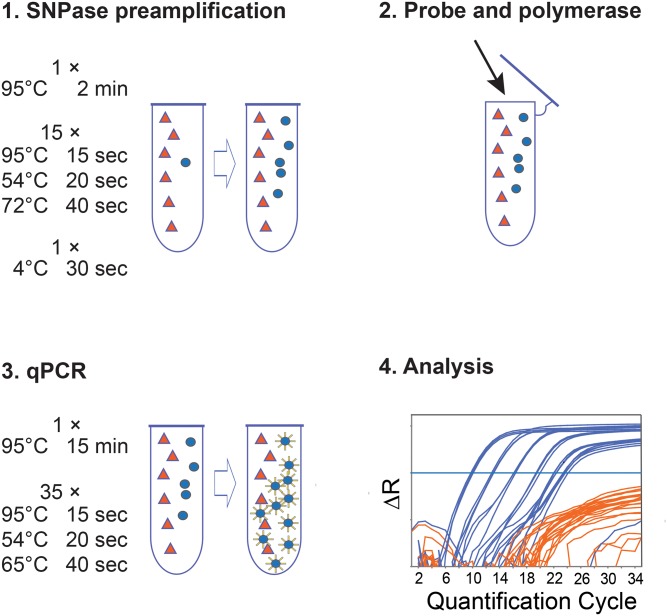
Fig 1. Workflow of SNPase-ARMS qPCR.
Fig 1 shows the workflow of SNPase-ARMS qPCR. 1. SNPase preamplification: with the SNPase polymerase, allele-specific primers amplify the target DNA based on the respective single nucleotide variant (SNV) with extreme sensitivity. In 15 PCR cycles the ratio between target (blue circles) and non-target (orange triangles) DNA is changed towards the target DNA. An exemplary temperature protocol for the BRAF V600E assay is shown. The last PCR cycle ends in a 4°C step to inhibit unspecific elongation. The PCR plate is put on ice immediately afterwards, and kept on ice during the next step. 2. Probe and Polymerase: the reaction tube (PCR plate) is opened (preferentially in a separate room to avoid contamination), and 5′ to 3′ exonuclease active polymerase and hydrolysis probe are added. 3. qPCR: in this step, the already preamplified target gene is amplified by the 5′ to 3′ exonuclease active polymerase. The initial step, 95°C for 15 minutes, inhibits the residual SNPase polymerase, and activates the newly added hot-start polymerase. During the following standard qPCR, the sequence-specific hydrolysis probe is cleaved and a fluorescence signal corresponding to the number of cleaved probes is created (symbolized by blue circles with a yellow corona). An exemplary temperature protocol for the BRAF V600E assay is shown. 4. Analysis: the qPCR is evaluated via the amplification plot. Quantification of positive samples is performed with the standard curve method [37] using the ViiA™ Software, v1.2.4.