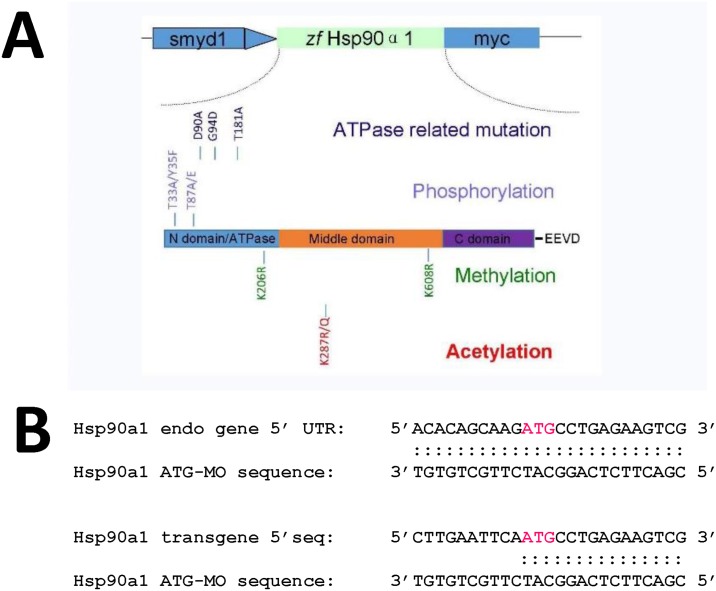
Fig 1. The schematic structure of various Hsp90α1 mutant constructs, and the sequence comparison of Hsp90α1 ATG-MO target in the endogenous Hsp90α1 gene and the Hsp90α1 transgenes.
A. The schematic structure of a zebrafish Hsp90α1 transgene expressing a myc-tagged Hsp90α1 under the control of the muscle specific smyd1 promoter. The Hsp90α1 contains 3 conserved functional domains. The N-terminal ATP binding and activation domain; the middle domain involved in cochaperone and client protein binding, and the C-terminal dimerization domain. Single and double mutations were made at the amino acid residues involved in ATP binding (D90, G94, T181), post-translational modification by phosphorylation (T33, Y35, T87), acetylation (K287) or methylation (K206, K608). The amino acid substitutions and their positions are indicated. B. DNA sequence comparison of Hsp90α1 ATG-MO target in the endogenous gene and the Hsp90α1 transgene. Half of the ATG-MO target sequence in the Hsp90α1 transgene has been replaced with an EcoRI site and part of the myc-tag sequence from the CS2-MT vector.