FIGURE 3.
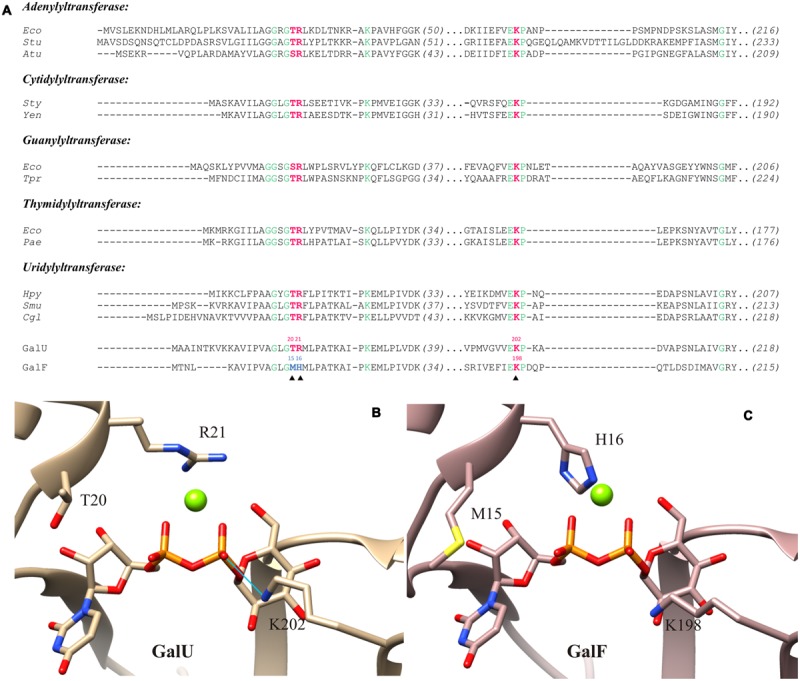
Active site models of GalU and GalF. (A) Sequence comparison of the UDP-Glc PPases (GalU and GalF) from Escherichia coli with pyrophosphorylases of different organisms. Residues 100% conserved are in green. Key residues analyzed in this study are in red. The key residues from GalF that are not conserved are shown in blue. Sequences and their accession numbers of adenylyltransferases (ADP-Glc PPase, EC: 2.7.7.27) are: Eco, E. coli K-12, P00584; Stu, Solanum tuberosum small subunit, P23509; Atu, Agrobacterium tumefaciens, P39669. Sequences and their accession numbers of cytidylyltransferases (α-D-glucose-1-phosphatecytidylyltransferase, EC: 2.7.7.33) are: Sty, Salmonella typhi, 1TZF; Yen, Yersinia enterocolitica, LC20, AHM71362. Sequences and their accession numbers of guanylyltransferases (GDP-mannose 1-phosphate guanylyltransferase, EC: 2.7.7.22) are: Eco, E. coli K-12, AAC75110; Tpr, Treponema primitia, WP_015708896. Sequences and their accession numbers of thymidylyltransferases (dTTP:α-D-glucose-1-phosphate thymidylyltransferase, EC: 2.7.7.24) are: Eco, E. coli, WP_000783975; Pae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, WP_003105518. Sequences and their accession numbers of uridylyltransferases (UDP-Glc PPase, EC: 2.7.7.9) are: Hpy, Helicobacter pylori26695, 3JUJ_A; Smu, Streptococcus mutans, AGI47014; Cgl, Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032, NP_600109; GalU, E. coli, WP_000718996; GalF, E. coli, WP_001537247. (B) Structural model of GalU; the product, UDP-Glc, and the ion Mg2+ were inherited from C. glutamicum UDP-Glc PPase crystal structure (2PA4). Homology model shows key residues mutated in this study: T20, R21, and K202. The potential hydrogen bond between K202and the β-phosphate of the UDP-Glc is indicated by the blue line. (C) Homology model of GalF with the product and the cofactor added. Key residues are shown: M15, H16, and K198.
