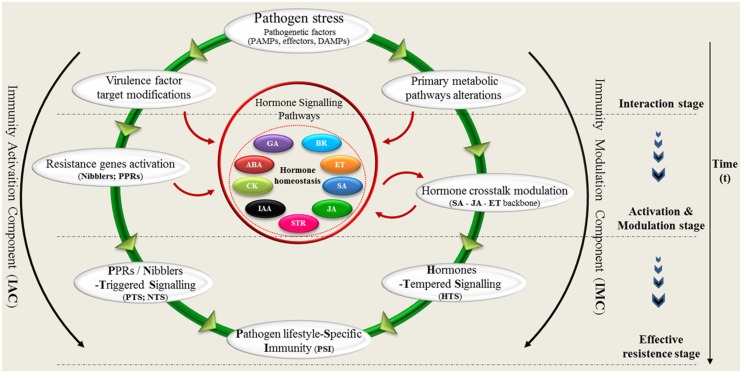
FIGURE 2.
The circular model. The model schematically shows the key points of activation and modulation of plant immunity. Plant resistance mechanism of an incompatible interaction might be divided into three phases: (1) interaction, (2) activation/modulation, and (3) effective resistance (immunity). During the interaction stage, two principal effects are detected: (A) modifications of virulence factor targets and (B) specific alterations of primary plant metabolism. In the activation stage: the modifications of virulence factor targets induce the Nibblers Triggered Signaling (NTS) or PPRs Triggered Signaling (PTS), mediated by R-genes activation. These metabolic alterations induce a feedback regulation of primary metabolic pathways resulting in a Hormone Tempered Resistance (HTR). In the effective resistance stage, the NTS/PTS, and the HTR converge to confer a resistance specific to the lifestyle of pathogen (Pathogen lifestyle-Specific Resistance, PSR).