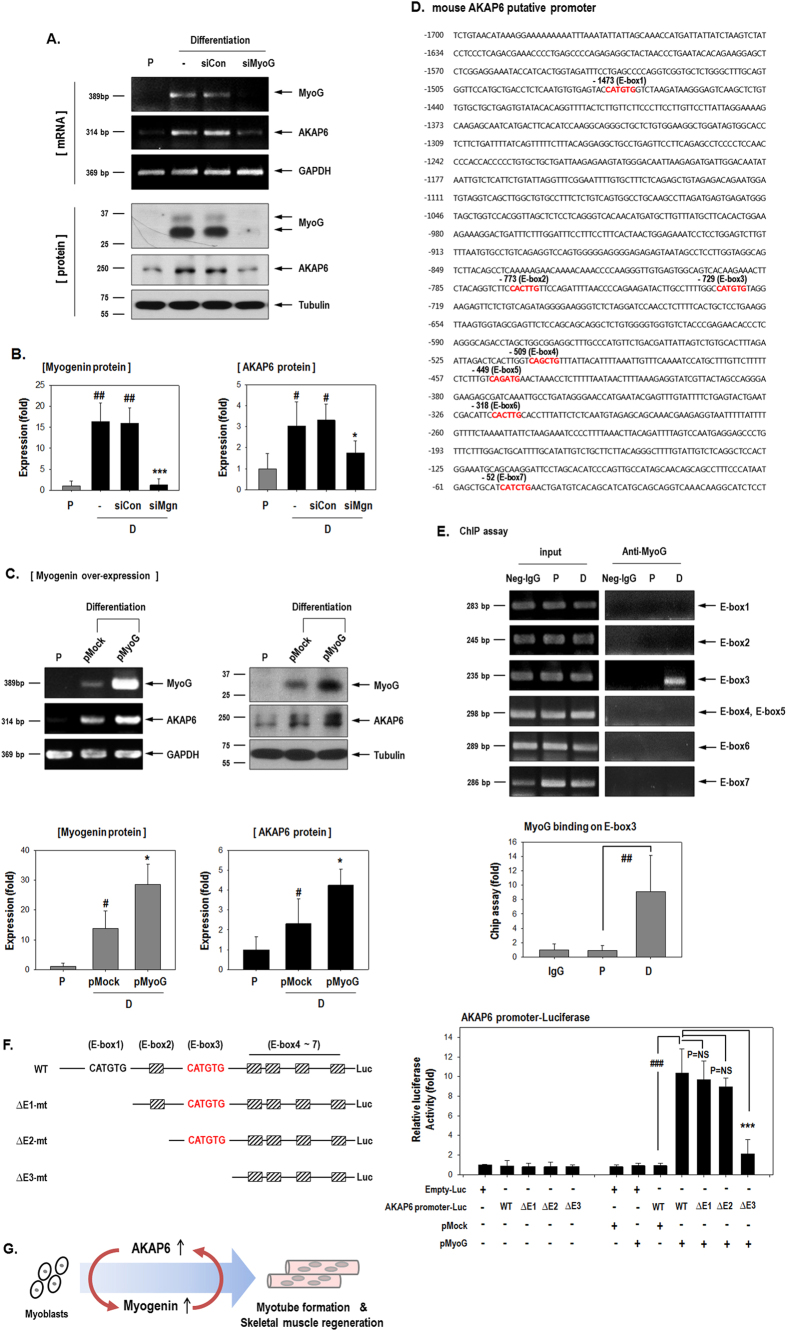
Figure 6. Myogenin transcriptionally increases AKAP6 by binding to an E-box on the AKAP6 promoter.
(A) Myogenin knockdown with siMyogenin (siMyoG) abolished the differentiation effect of AKAP6 up-regulation in C2C12 cells. (B) Quantification graphs for western blotting show relative fold changes over values under proliferation conditions (n = 4 each). #p < 0.05 and ##p < 0.01 versus proliferation; *p < 0.05 and ***p < 0.001 versus siCon + differentiation (one-way ANOVA). P, proliferation conditions; D, differentiation conditions. (C) C2C12 cells were transfected with pMyoG and incubated under differentiation conditions for 2 days. Myogenin overexpression increased AKAP6 mRNA and protein levels. Quantification graphs for western blotting show relative fold change over values under proliferation conditions (bottom, n = 5). #p < 0.05 versus proliferation; *p < 0.05 versus pMock + differentiation (one-way ANOVA). (D) Putative promoter sequence of mouse Akap6. Nucleotides are numbered relative to the translation start site, and the seven E-boxes (5′-CANNTG-3′) are marked in red. (E) Myogenin binds to the E-box 3 site. ChIP analysis showed myogenin binding to the AKAP6 promoter. C2C12 lysates were immunoprecipitated with a myogenin antibody. The precipitated DNAs were amplified with PCR by using specific primers for the E-box (n = 5 each). Quantification graph for ChIP assay on E-box 3 region (bottom, n = 5). The graph shows the relative fold changes over levels under proliferation conditions. ##p < 0.01 versus proliferation (one-way ANOVA). P, proliferation conditions; D, differentiation conditions. (F) Luciferase assay for myogenin binding to the AKAP6 promoter. Schematic diagram of the seven E-box sites in the full-sequence AKAP6 promoter and the promoter serial deletion mutants (Left). HEK293A cells were transfected with various combinations of WT-AKAP6-promoter, AKAP6 promoter deletion mutants, and myogenin plasmids, and the luciferase assay was performed (Right, n = 3 each). ###p < 0.001; ***p < 0.001 (one-way ANOVA). (G) Schematic representation of the importance of AKAP6 in skeletal muscle regeneration.