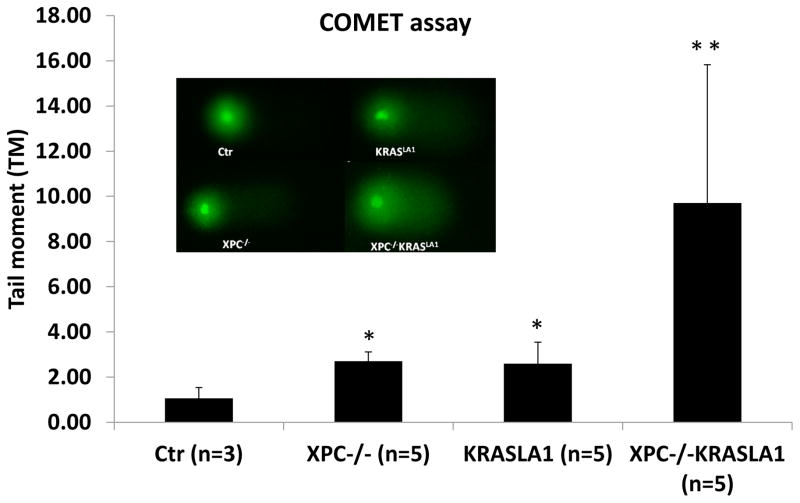
Fig. 4. DNA damage analysis in lung tissues from 2-months old mice with different genetic alterations.
A: Fresh lung tissues from the control, Xpc−/−, KrasLA1 and Xpc−/−KrasLA1 mice were processed to measure DNA damage using the COMET assay. Bronchial epithelial cells were isolated and subjected to COMET assay. For each sample, 200 independent cells were evaluated. The difference between the control mice and the other three groups (Xpc−/−, KrasLA1 or Xpc−/−KrasLA1) were significant (with a P value <0.05; as indicated by *). Data from the Xpc−/−KrasLA1 mice were significantly higher than mice with a single gene mutation (Xpc−/−or KrasLA1) (with a P value < 0.05, indicated by **) or the sum from two single mutant mice. According to BLISS independence analysis, Xpc loss and KrasLA1 expression had a more than additive effect (synergy) on induction of DNA damage.