Figure 6. SF-3-030 selectively inhibits ERK2-mediated c-Fos phosphorylation in an in vitro kinase assay.
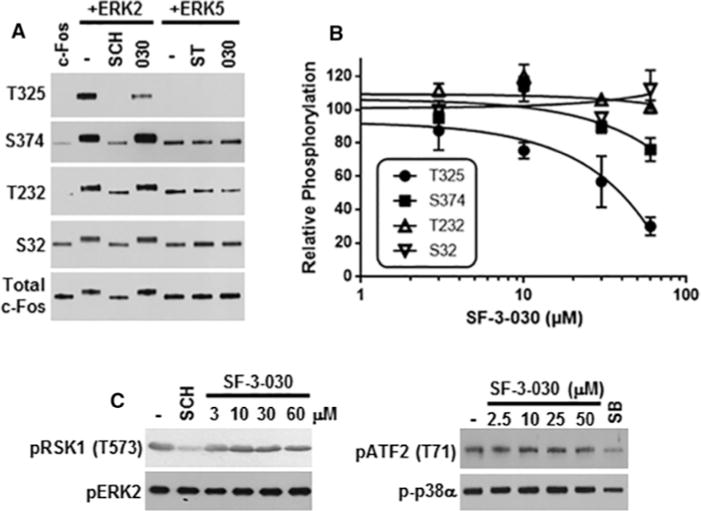
(A) Active ERK2 or ERK5 were pre-incubated in the absence or presence of 50 μM SF-3-030 (030), 10 μM SCH772984 (SCH) or 10 μM staurosporine (ST) followed by initiation of the kinase assay with the addition of c-Fos substrate and ATP. After 30 min of incubation, the reaction was stopped and the c-Fos phosphorylation sites indicated were evaluated by immunoblotting. (B) Densitometry analysis of ERK2-mediated c-Fos phosphorylation on Thr325, Ser374, Thr232 and Ser32 in the presence of 3–60 μM SF-3-030. Data are normalized to ERK2-mediated c-Fos phosphorylation in the presence of vehicle (DMSO) only. (C) Immunoblot analysis of in vitro kinase assays for ERK2-mediated RSK1 phosphorylation (pRSK1 Thr573) or p38α MAPK-mediated phosphorylation of ATF2 (pATF2 Thr71) in the absence or presence of 2.5–60 μM SF-3-030. Controls for ERK2 or p38α kinase activity include 1 μM SCH772984 (SCH) or 10 μM SB239063 (SB) respectively. The levels of phosphorylated ERK2 or p38α are shown for each condition.
