Table 1.
Evaluation of the Conjugate Addition under Lewis Acidic Conditions
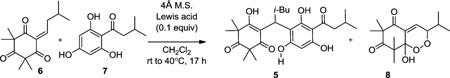 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| entrya | Lewis acid | 5:8c | 5 (%)b |
| 1 | no catalyst | 1:2.7 | 9 |
| 2 | YbCl3 | 1.15:1 | 38 |
| 3 | FeCl3 | 1.3:1 | 36 |
| 4 | Yb(OTf)3 | 1:3.3 | 16 |
| 5 | Gd(OTf)3 | 1:2.4 | 29 |
| 6 | Lu(OTf)3 | 1:1.7 | 17 |
| 7 | Cu(ClO4)2 | 1:4.3 | 6 |
| 8 | Mg(ClO4)2 | N/A | 0 |
| 9 | Zn(ClO4)2 | N/A | 0 |
| 10 | PdCl2(PhCN)2 | N/A | 19 |
| 11 | Ni(ClO4)2·6H2O | 4.6:1 | 74 |
| 12 | Ni(ClO4)2·6H2O (7 mol %) CH2Cl2:AcOH (6:1) | 2.8:1 | 80 |
| 13d | Ni(ClO4)2·6H2O (7 mol %) CH2Cl2:AcOH (6:1) | 1:0 | 90 |
Reactions conducted with monoalkylidene 6 (1 equiv) and acylphloroglucinol 7 (1.5 equiv) in 1 mL of CH2Cl2.
Yields reported after isolation by silica gel column chromatography.
Compound 8 was the only byproduct observed after complete consumption of starting materials. Ratio was determined after isolating both products.
Solvents were thoroughly degassed using the freeze–pump–thaw method.
