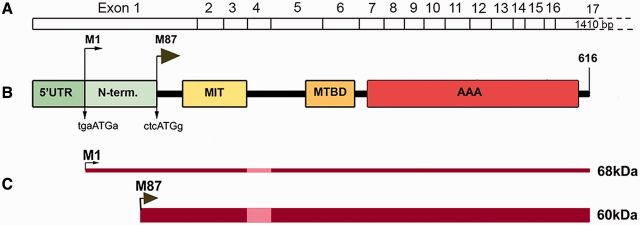
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of spastin structure. (A) Spastin exons 1–17. (B) Spastin functional domains: N-term = N-terminal sequence present only in M1 spastin isoform; MIT = microtubule interacting and trafficking domain; MTBD = microtubule-binding domain; AAA = ATPase associated with various cellular activities. The Kozak’s sequence tgaAUGa surrounding M1 start codon deviates considerably from a good consensus sequence g(a)ccAUGg. A better Kozak sequence ctcAUGg is present at the M87 initiation codon. (C) A leaky scanning of the first initiation codon with a poor Kozak’s sequence leads to a preferred initiation of translation at the second AUG. As a result, both 68 kDa M1 and 60 kDa M87 spastin isoforms are expressed simultaneously but at different levels. A thin dark red line represents low levels of M1 expression and a dark red bar represents considerably higher levels of M87. Light red represents the M1 and M87 regions that are not present in spastin isoforms encoded by alternatively spliced mRNA lacking exon 4.