Fig. 3. Latencies of motor skill acquisition are predicted by the interaction between the amount and the intensity of locomotor play before the acquisition.
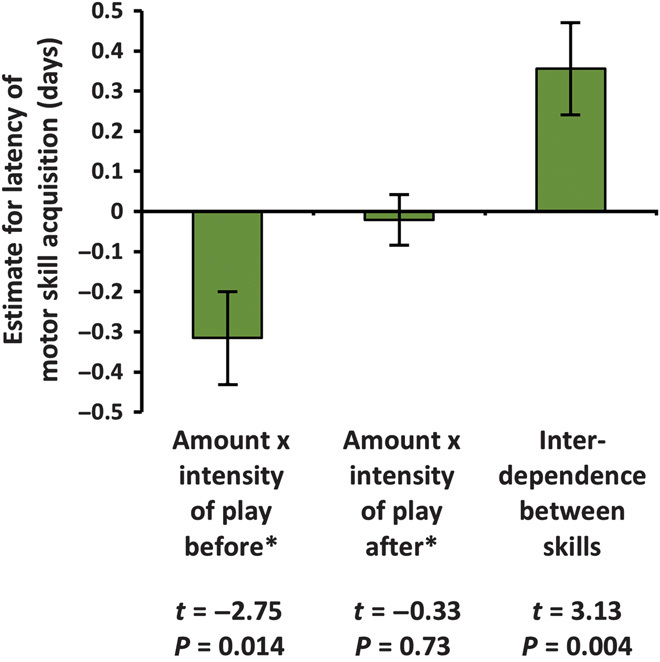
Estimates ± SD of the z-transformed variables predicting latency of motor skill acquisition of 16 skills (LMM, n = 184). Random factor: motor skill labels; model significance: P = 0.014, R2 = 0.715; intercept: estimate 8.2 ± 0.4. *Before/after the respective age of motor skill acquisition. Sex of the infant was not significant and thus excluded from the model.
