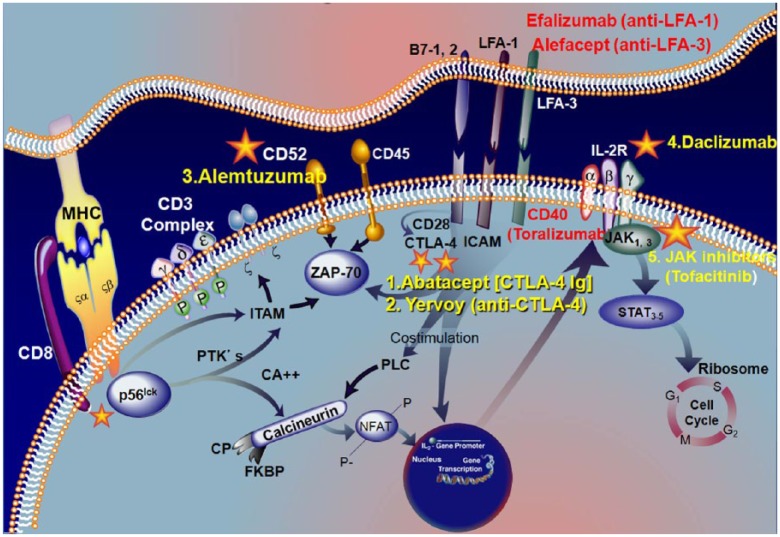
Figure 2.
Signaling pathways activated by major histocompatibility complex (MHC)/T-cell receptor (TCR) engagement and successful drugs (1–4) that inhibit specific signaling molecules (expansion of box 1 in Figure 1b).
The interaction of TCR with antigen/MHC complex activates intracellular phosphotyrosine kinases (ZAP-70) that mediate signaling via phosphorylation of immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs (ITAMs) and transduction molecules such as CD52. T-cell activation is meditated via costimulatory factors delivered by LFA-I/ICAM and LFA-3/CD2, CD40 and CD28/CTLA-4 interactions. Monoclonal antibodies against LFA1 [efalizumab (Raptiva)] and anti-CD40 (toralizumab) or fusion proteins against LFA3 [alefacept] that block the T-cell activation process have either failed or withdrawn from the market (see text). However, two drugs in this group targeting CTLA-4, abatacept and yervoy [Vincent and Rothwell, 2004; Engel, 2006] have been effective and are approved. TCR engagement and costimulation activates sequentially downstream events that, via phospholipase (PLC) and activation of calcineurin, activate the nuclear factor of activated T cells, which is translocated into the nucleus where it binds to interleukin (IL) 2 promoter to induce cell proliferation and differentiation. Antibodies against CD52 alemtuzumab (3*) can stop the T0cell activation. Activated T cells synthesize the T-cell growth factor, IL-2 and its receptor, which binds to IL-2 with moderate affinity. This receptor can be blocked by the monoclonal antibody to CD25 [daclizumab (4*)]. Binding of IL-2 to the receptor in turn activates an intracellular signaling cascade via Janus kinases (JAK1, JAK3), with subsequent phosphorylation of signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) proteins. The compound against JAK kinases (tofacitinib [5*]) inhibits IL-2 dependent differentiation of helper T cells and suppresses B and T cell functions [adapted from Aricha et al. 2011; Masuda et al. 2010; Dalakas, 2010b, 2011a, 2011b]. The asterisks denote the approved drugs on the market (extensively modified from Dalakas 2013).
CTLA-4, cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen; ICAM, intercellular adhesion molecule; LFA-1, lymphocyte function antigen 1; LFA-3, lymphocyte function antigen 3; NFAT, nuclear factor of activated T cells; PLC, phospholipase C; PTK, protein tyrosine kinase; ZAP-70, zeta-chain associated protein 70.