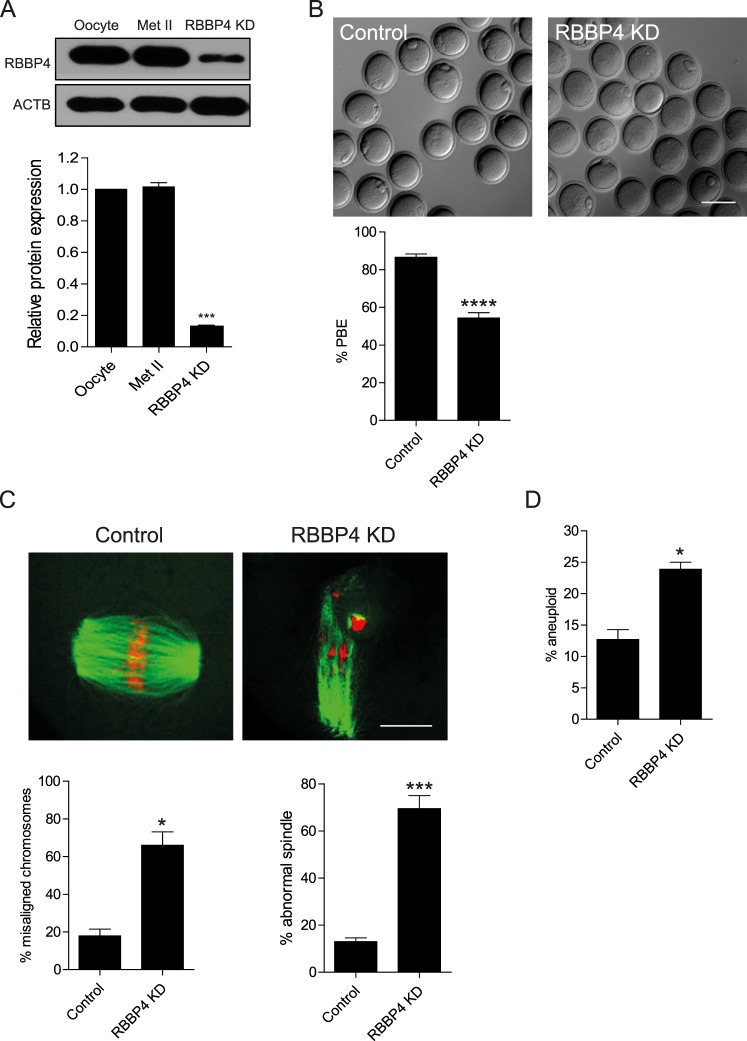
FIG. 2.
Knockdown of RBBP4 perturbs meiotic progression and chromosome segregation. A) Full-grown, GV-intact oocytes were injected with the siRNA and morpholino cocktail, followed by maturation in vitro for 18 h. A) Fifty oocytes and Met II eggs were collected for immunoblot analysis, and β-actin (ACTB) was used as a loading control. The experiments were carried out five times. The quantification of the abundance of RBBP4 is shown. The data are expressed as the mean ± SEM, and one-way ANOVA was used to analyze the data. B) First PBE was scored to assess meiotic progression. C) Fixation and staining of spindle with an anti-β-tubulin antibody (green) and DNA with TOPRO-3 (red) were performed using confocal microscopy. Representative images are shown. The confocal images were analyzed for both the percentage of misaligned chromosomes and abnormal spindle morphology (below). D) Met II eggs were treated with Monastrol for 2 h to induce monopolar spindles, followed by kinetochore staining with CREST antiserum and DNA staining with TOPRO-3. Met II eggs with greater or less than 40 kinetochores were considered to be aneuploid. The experiments were carried out at least three times, and at least 20 oocytes were examined for each treatment group. The data are expressed as the mean ± SEM. Student t-test was used to analyze the data. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. Bar = 100 μm (B) and 10 μm (C).