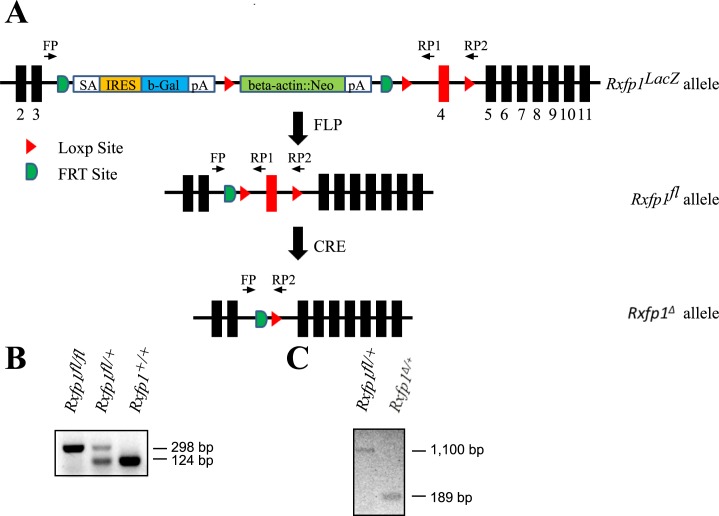
FIG. 1.
LacZ knockin and floxed alleles of Rxfp1. A) Schematic representation of Rfxp1LacZ, Rxfp1fl, and Rxfp1Δ alleles. Exons are shown as black boxes and marked by a number underneath. SA is a splicing acceptor; IRES is an internal ribosome entry site; b-Gal is a β-galactosidase gene; pA is a poly(A) signal; beta-actin::Neo is neomycine-resistant gene driven by β-actin promoter; FLP is flp recombinase; CRE is cre recombinase. There are three LoxP sites for Cre recombinase on the 5′ and 3′ ends of the neo cassette and within intron 4. Rxfp1fl allele is produced by flp-induced recombination, and the deleted allele without exon 4 is produced by cre-induced recombination as shown. The position of the primers used for genotyping is shown with arrows. B) Detection of Rxfp1fl floxed allele with primers FP/RP1. The floxed allele produced a 298-bp band and the wild-type allele produced a 124-bp band. C) Detection of Rxfp1Δ deleted allele with FP/RP2 primers. The floxed allele produced a 1100-bp band and the deleted allele produced a 189-bp band. The wild-type allele is not detectable with this primer pair.