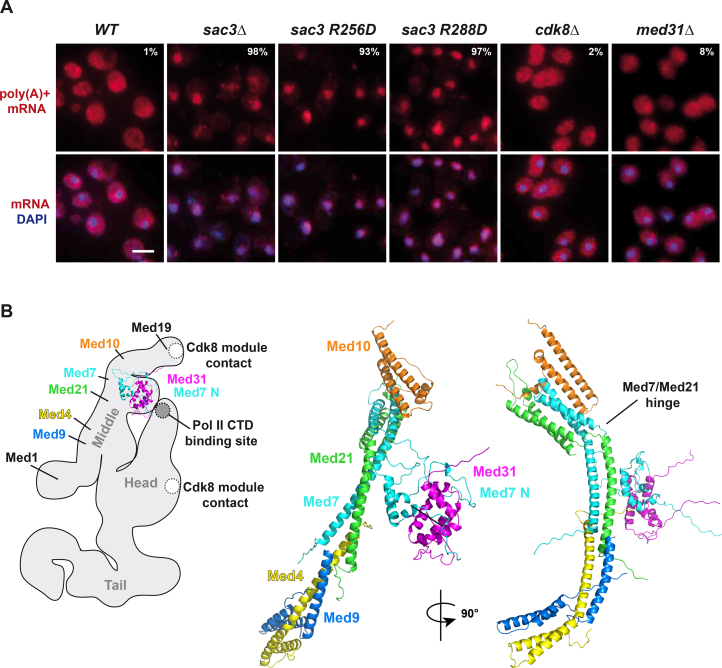
Figure S7.
mRNA FISH Analysis and Model of the Mediator Middle Module, Related to Figures 3, 4, and 5
(A) Analysis of nuclear mRNA export in the indicated wild-type and mutant strains, containing the respective plasmids. Exponentially growing cells were subjected to poly(A)+ RNA fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) with Cy3-labeled oligo probes. DNA was stained with DAPI. Percentage numbers indicate cells with nuclear fluorescent intensity above cytoplasmic signal (n = 100). Scale bar, 4 μm.
(B) Left: cartoon of the yeast Mediator complex cryo-EM structure (Tsai et al., 2014). Subunits of the ‘middle‘ module are indicated based on the deletion, labeling, and crystal structure docking analysis performed in that study. Approximate positions of the Pol II CTD binding site (Robinson et al., 2012, Tsai et al., 2014) and two prominent Cdk8 kinase module contact points (Tsai et al., 2013) are marked. Right: structural model of yeast Mediator ‘middle‘ module (Lariviere et al., 2013). The Med31/Med7N submodule in the left structure has the same orientation as the submodule docked into the cryo-EM based cartoon. Note that the Med31 submodule is flexibly connected to the elongated ‘middle‘ backbone, which itself contains a conserved flexible hinge (Baumli et al., 2005). TREX-2 docking onto the Med31 submodule is proposed to induce conformational changes in this part of Mediator.