Figure 6.
Constitutive Activation and Inactivation of Kinases by NAMs
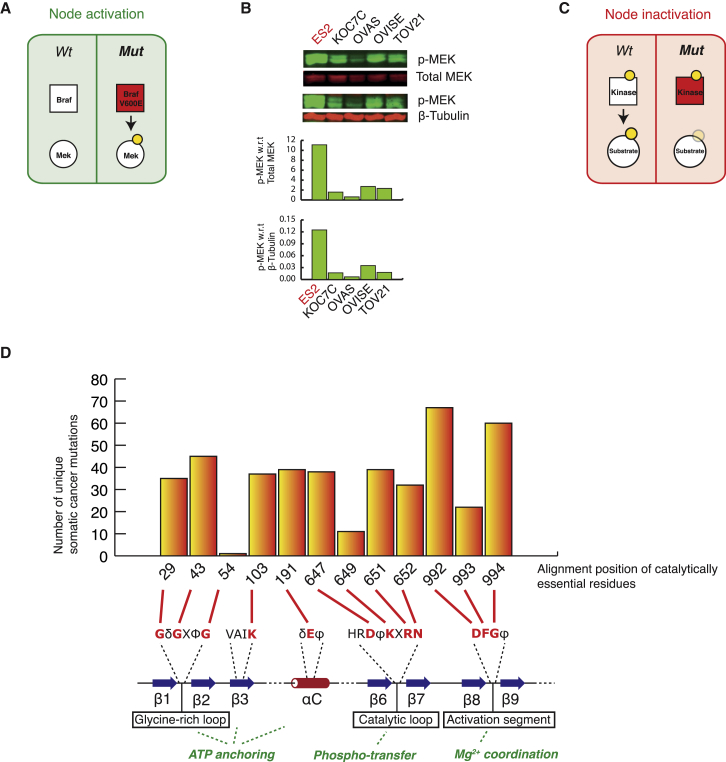
(A) ReKINect identified ES2 cells as containing the constitutively activating BRAF V600E mutation.
(B) An immunoblot and associated quantification, illustrating the phosphorylation of BRAF substrate MEK in the mutant cell line ES2 (in red) compared to the wild-type cell lines (in black), using total MEK and β-tubulin for normalization.
(C) ReKINect identified several cancer mutations in catalytically essential residues of kinase domains.
(D) A quantification of all mutations from the global repository of cancer somatic mutations predicted to inactivate kinases and the catalytically essential positions they hit. Mutations leading to kinase domain catalytic inactivation are enriched (χ2 test, p = 1.69 × 10−16) in cancer somatic mutations (with particular preference for the aspartate, D, and glycine, G, in the DFG motif).