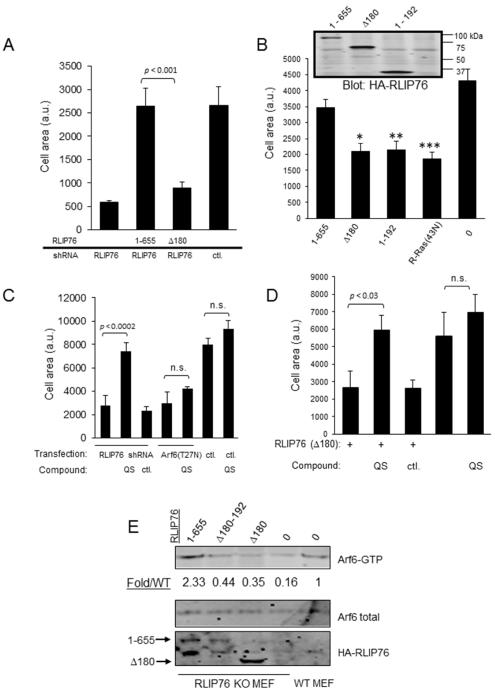
Fig. 3. The RLIP76 N-terminus is required for efficient cell spreading upstream of Arf6.
(A – D). Cells were transfected as indicated and seeded on fibronectin-coated surfaces for spreading assays. HA-RLIP76 expression levels are shown in the inset panel in (B). (0) = vector control. *, p < 0.02; **, p < 0.004; ***, p < 0.001 (n=3). The average surface areas of GFP-positive cells are shown + SEM (n=3). (C,D) Cells were treated with 1 μM of either QS11 (QS) ArfGAP1 inhibitor or QS11-NC inactive control compound (ctl.), and assayed for spreading. (E) Arf6 activation in cells transfected with the indicated RLIP76 consdtructs, shown as fold increase in the ratio of GTP-Arf6 to total Arf6, normalized to WT (Fold/WT). Representative of four independent experiments.