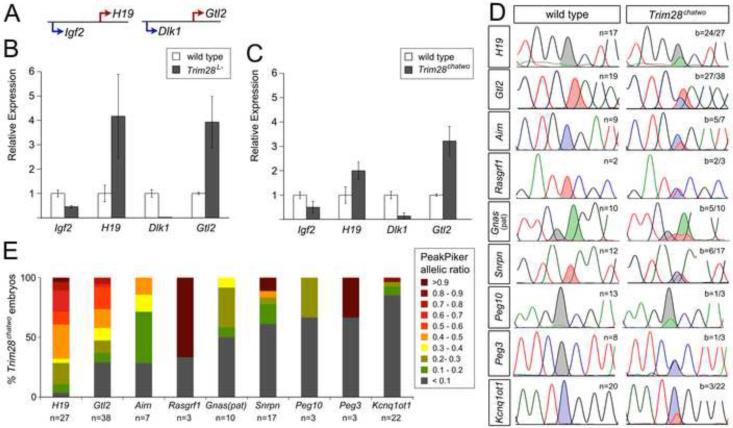
Figure 1. Imprinted gene expression in zygotic Trim28 mutants.
(A) Diagram of the Igf2-H19 and Dlk1-Gtl2 clusters, indicating maternally (red) and paternally (blue) expressed genes. (B-C) Expression of imprinted genes in the Igf2-H19 and Dlk1-Gtl2 clusters as determined by qRT-PCR in pools of 3-4 E7.5 Trim28L- (B) and E8.5 Trim28chatwo (C) embryos. Data shown is normalized to ß-actin and relative to wild type controls. Error bars represent the standard deviation from two biological replicates. (D) Selected Sanger sequencing traces of cDNAs for H19, Gtl2, Airn, Rasgrf1, Gnas (paternal isoform), Snrpn, Peg10, Peg3, and Kcnq1ot1 in individual E8.5 wild type and Trim28chatwo embryos containing allele-specific SNPs (shaded peaks). All imprinted genes were analyzed in embryonic tissues, except for Rasgrf1, which is only imprinted in E8.5 extraembryonic tissues (Dockery et al., 2009). b = embryos with biallelic expression over the total number of embryos analyzed. (E) Percent of Trim28chatwo embryos with biallelic expression of imprinted genes as analyzed by Sanger sequencing and quantified using PeakPicker. Wild type embryos showed PeakPicker allelic ratios between 0-0.1. Values higher than 0.1 were considered biallelic. A value of 1 corresponds to equal expression from both alleles. n = total number of embryos analyzed.