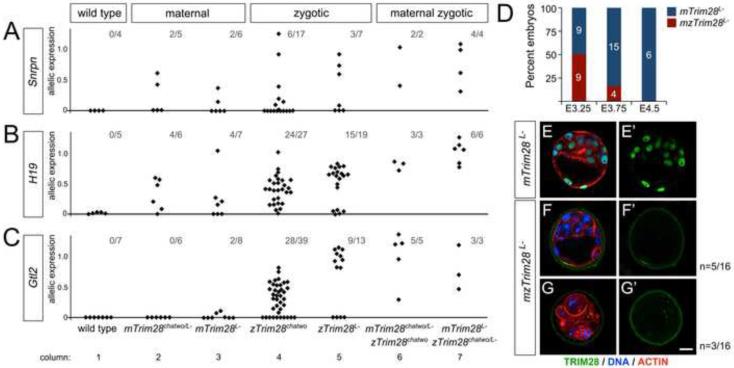
Figure 2. Analysis of maternal, zygotic, and maternal-zygotic Trim28 mutants.
Allelic expression in wild type, maternal (mTrim28chatwo/L- and mTrim28L-), zygotic (zTrim28chatwo and zTrim28L-), and hypomorphic maternal-zygotic (mTrim28L- - zTrim28chatwo/L- and mTrim28chatwo/L- - zTrim28chatwo) Trim28 mutants was analyzed at Snrpn (A), H19 (B), and Gtl2 (C) by Sanger sequencing and quantified with PeakPicker. Each diamond represents a single embryo. The fractional numbers indicate the number of mutants with biallelic expression over the total number of embryos analyzed. All embryos were analyzed at E8.5 except for zTrim28L- and hypomorphic maternal-zygotic mutants, which were analyzed at E7.5. Analysis of wild type samples at E7.5 and E8.5 showed similar results (not shown). (D) Percentage of mTrim28L- (blue) and mzTrim28L- (red) mutants found in dissections at E3.25 (n=18), E3.75 (n=19), and E4.5 (n=6). (E-G) Fluorescence staining of TRIM28 (green), DNA (DAPI, blue), and ACTIN (phalloidin, red) in mTrim28L- (E) and mzTrim28L- (F-G) blastocysts. TRIM28 localization (green channel) is shown separately in E’-G’. Scale bar = 20µm.