Figure 1.
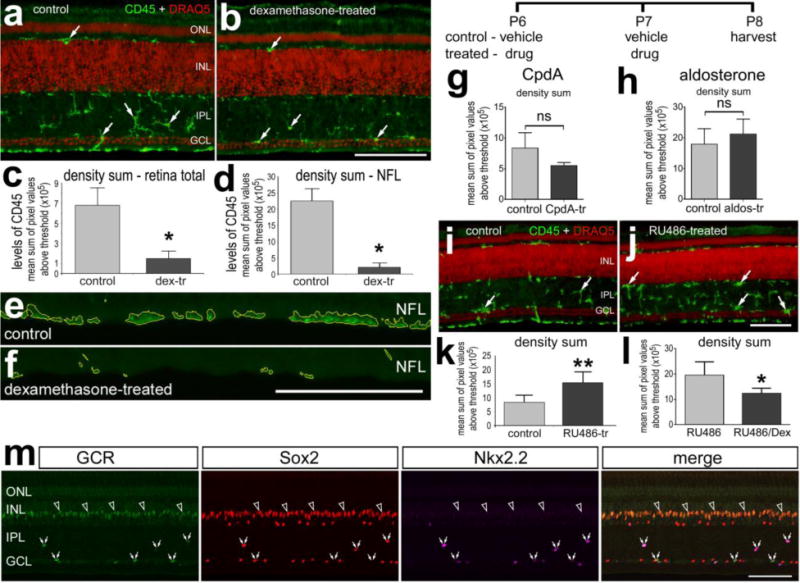
In undamaged retina activation of GCR inhibits, whereas inhibition of GCR activates microglial reactivity. Retinas where obtained from eyes that received 2 consecutive daily injections of Dex (a–f), CpdA (g), aldosterone (h), RU486 (i–k) or vehicle, or the combination of Dex and RU486 or RU486 (l). Tissues were harvested 24 hours after the last injection. Sections of the retina were labeled with DRAQ5 (red; a,b,i,j), antibodies to CD45 (green;a,b,e,f,i,j) or GCR, So×2 and Nk×2.2 (m). In m the immunolabeling was done on normal untreated retinas. e and f; areas about threshold are outlined by yellow. Quantitative immunofluorescence was used to measure the density sum of CD45-immunofluorescence (c,d,g,h,k,l). The histograms illustrate the mean (±SD; n≥5) density (intensity) sum. Arrows indicate reactive microglia (a,b,i,j), hollow arrows indicate the nuclei of GCR+ Müller glia in the INL, and small double-arrows indicate GCR+ NIRG cells in the IPL and GCL (m). All the scale bars are 50 μm. The scale bar in panel b applies to a and b, the bar in f applies to e and f, the bar in j applies to i and j, and the bar in m applies to m alone. Abbreviations: ONL – outer nuclear layer, INL – inner nuclear layer, IPL – inner plexiform layer, GCL – ganglion cell layer, NFL – nerve fiber layer. Significance of difference (*p<0.05; ns – not significant) was determined by using a two-tailed t test.
