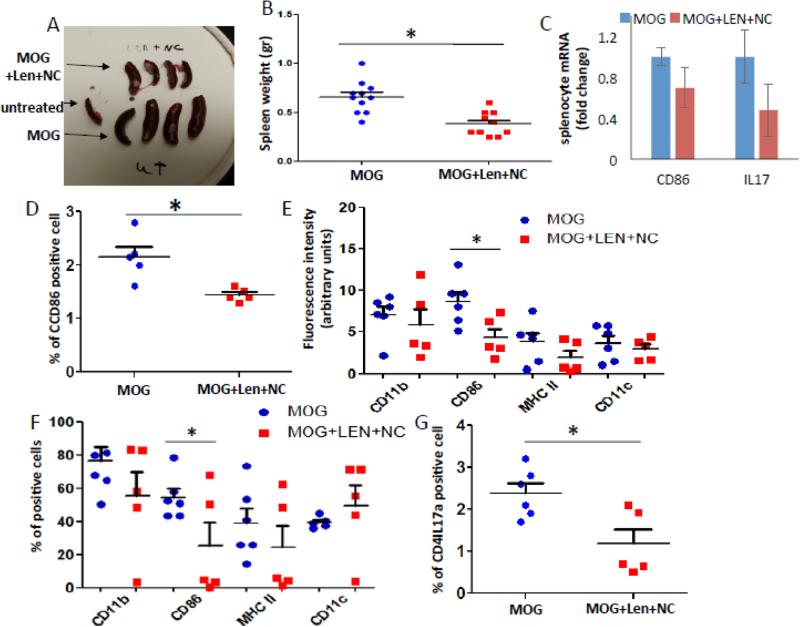
Figure 7.
Combination therapy with lenalidomide and nanoceria inhibits dendritic cell activation in the spleen. A. Images of spleens taken from mice immunized with MOG and treated either lenalidomide and nanoceria or vehicle for 10 days. B. Spleen weights. C. RNA was isolated from the spleens and the relative levels of mRNA encoding the cytokines IL-17 and coactivation factor CD86 were determined by qRT-PCR. D. Splenocytes were isolated from the spleens and the levels of CD86 expressing cells was measured by FACS. E-G. Splenocytes were cultured for 72 hours in the presence of MOG and IL23. Lenalidomide and nanoceria were added to the culture medium of splenocytes from mice that had received combined treatment, and vehicle was added to the medium of splenocytes from mice that had received vehicle. Cells were stained with antibodies against CD11b, C86, MHC-II and C11c and the average intensity of immunoreactivity for each antigen was quantified (E), the percentage of cells (counted by DAPI) that express each protein was determined (F), and the percentage of T cell that express IL17a was measured by FACS (G). *p<0.05 compared by Student's t test. NC-nanoceria; Lenlenalidomide.