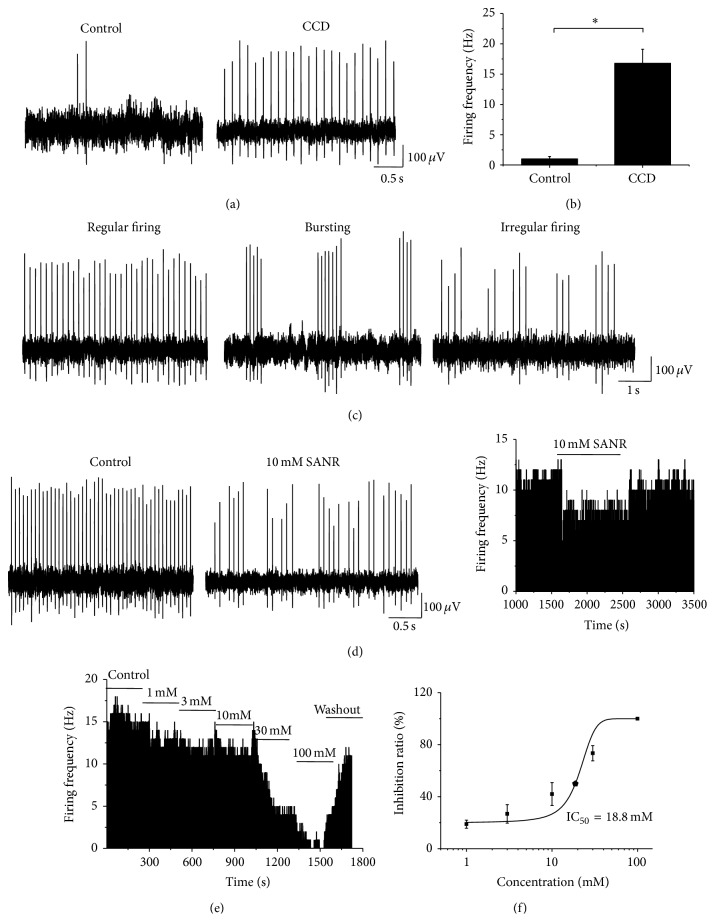
Figure 7.
SANR produces dramatic inhibition on ectopic spontaneous discharges of the injured DRG neurons in CCD rats. (a) Following chronic compression of DRG, primary afferent A fibers of DRG neurons frequently exhibited ectopic spontaneous discharges (right panel); this rarely happens in sham control rats (left panel). (b) Quantitative analysis of the rate of spontaneous discharges in A-type DRG neurons derived from CCD and control rats. (c) According to the dynamic features of interspike interval series, three different firing patterns were observed, which are regular (left panel), bursting (middle panel), and irregular patterns (right panel). (d) Representative traces showing that bath application of SANR (10 mM) (middle panel) produces marked depression of spontaneous discharge rate compared to vehicle in the same cell (left panel). Frequency histogram on the same cell was shown in the right panel. (e) Frequency histogram showing a dose-dependent inhibition of ectopic spontaneous discharges by SANR in a reversible manner. (f) Analysis of the curve based on the Hill plot yielded an IC50 of 18.8 mM for SANR.