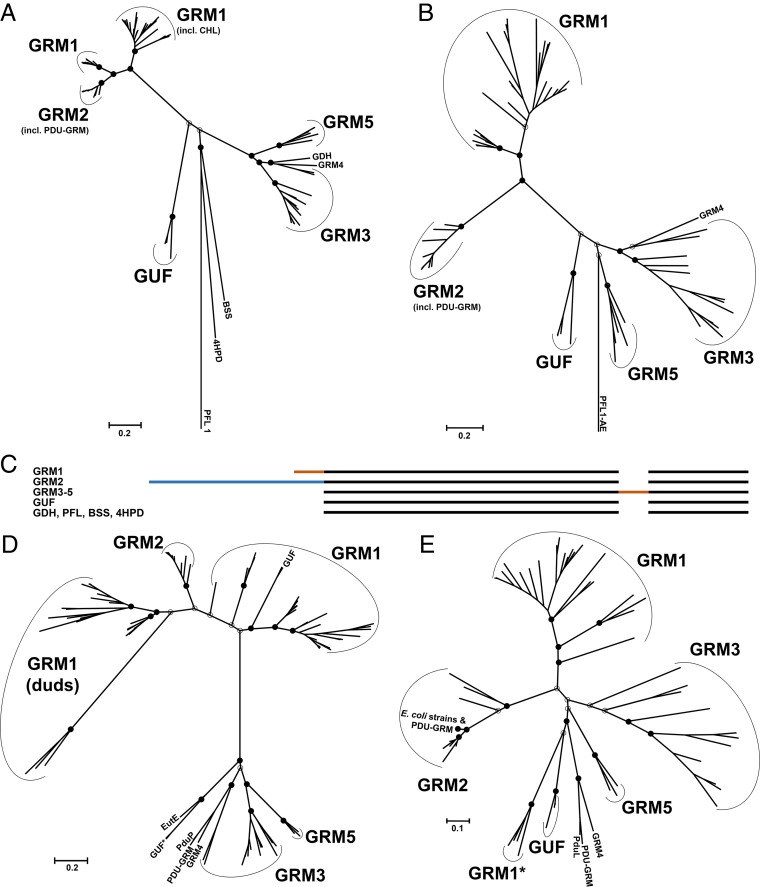
FIG 2.
Phylogenetic trees of GRM-associated enzymes. Maximum likelihood trees are drawn to scale, and branch lengths are based on the number of substitutions per site. Bootstrap values for important nodes are represented as filled circles (above 50%) and empty circles (below 50%). (A) GRE tree generated from 83 amino acid sequences. The sequences used for calibration were those of biochemically characterized GREs not associated with BMCs: vitamin B12-independent glycerol dehydratase (GDH) from Clostridium butyricum, the benzylsuccinate synthase (BSS) from Thauera aromatica, the 4-hydroxyphenylacetate decarboxylase (4HPD) from Clostridium difficile, and pyruvate formate-lyase type 1 (PFL1) from E. coli. PDU-GRM, the locus in Escherichia fergusonii which appears to be a fusion of the PDU BMC and GRM loci; GUF, GREs of unknown function; CHL, choline TMA-lyase. (B) Tree of the activating enzymes inferred from 79 amino acid sequences. The activating enzyme of the pyruvate formate-lyase type 1 from E. coli (PFL1-AE) was used as an outgroup. (C) Cartoon representation of the multiple-sequence alignment of the GREs. Orange segments, extensions/insertions that likely constitute EPs with linkers; blue segment, the N-terminal extension of the GREs of the GRM2 BMCs that appears to be a partial domain duplication. (D) Tree of the acylating aldehyde dehydrogenases (AldDHs) inferred from 111 amino acid sequences. The AldDH homologs from the conventional ethanolamine-utilizing BMC (EutE) and propanediol-utilizing BMC (PduP) from Salmonella enterica were included in the analysis. GRM1 (duds), presumably inactive AldDH homologs; GUF*, AldDHs from D. psychrophila. (E) Tree of PduL-like phosphotransacylase homologs inferred from 74 amino acid sequences. The phosphotransacylase (PduL) from the experimentally characterized PDU BMC of S. enterica was included for comparison. GRM1*, the PduL homologs of Desulfovibrio spp.