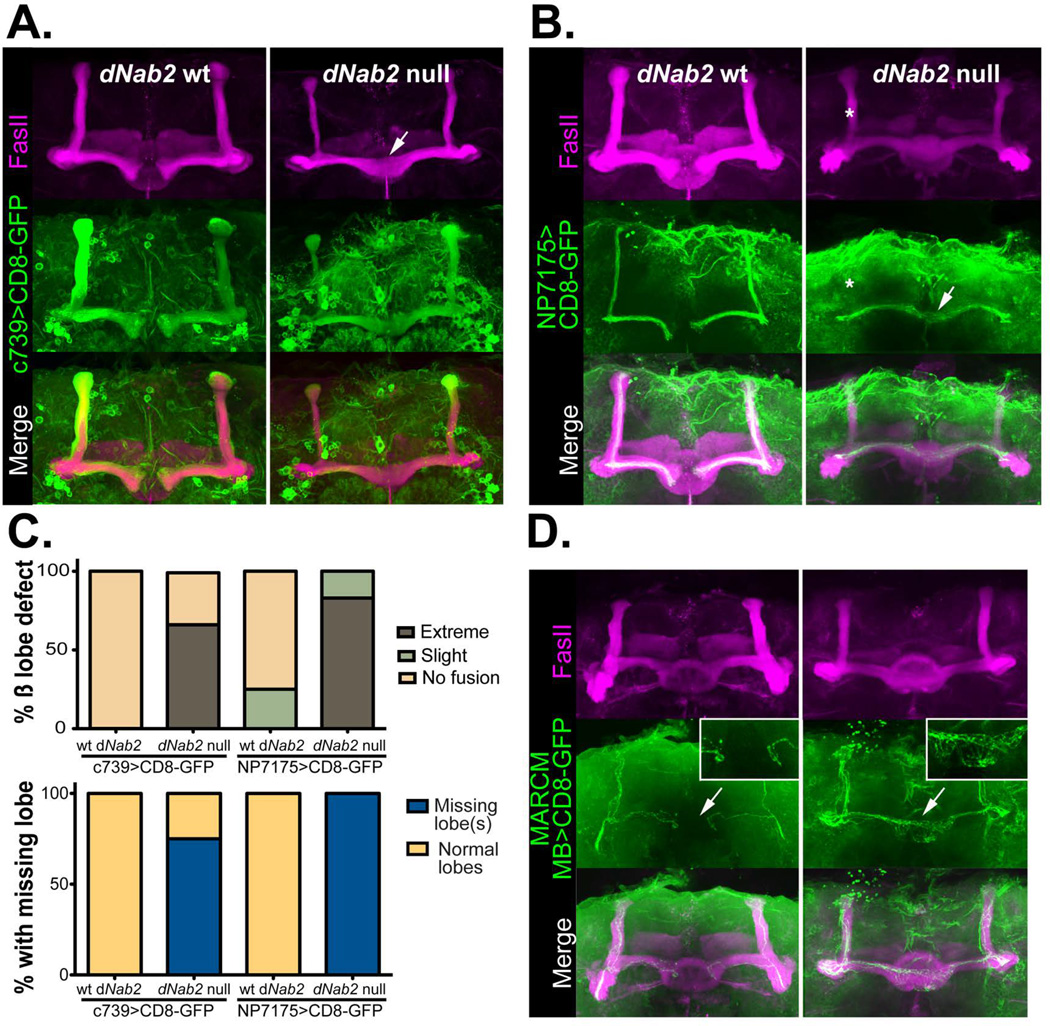
Figure 2. Loss of dNab2 disrupts the morphology of Drosophila mushroom body neurons.
UAS-CD8-GFP (green) was used in combination with cell-type specific Gal4 drivers to mark either all α/β neurons (A; c739) or “core” α/β neurons (B; NP7175) of the MBs in dNab2pex41 control or dNab2ex3 null brains. Brains are co-stained with FasII (magenta) to mark of the α/β lobes. Control β-lobes terminate at the brain midline but lobes from dNab2ex3 null brains overextend into the contralateral hemisphere (white arrows). α-lobe core axons are often absent in dNab2ex3 null brains (white asterisk). Genotypes shown are: (A) C739-Gal4/UAS-CD8-GFP;+/+ or C739-Gal4/UAS-CD8-GFP;dNab2ex3/dNab2ex3 and (B) NP7175-Gal4/Y;UAS-CD8-GFP/+;+/+ or NP7175-Gal4/Y;UAS-CD8-GFP/+; dNab2ex3/dNab2ex3. C, Quantification of the frequency of the β-lobe midline fusion defects (top) and the missing α- or β-lobe defects observed in A and B. Phenotypes were scored according to the criteria outlined in (Michel et al., 2004). Mushroom body β lobes show ‘extreme fusion’ when lobes cross the midline with similar or increased thickness to the rest of the β-lobe (white arrows in A and B). Brains showing thin β-lobes crossing the midline in comparison to the thickness of β-lobes of either side of the midline are scored as having ‘slight fusion.’ D, MARCM analysis of individual neurons (green) in dNab2 control and dNab2ex3 null brains co-stained with FasII (magenta). Wildtype β-axons terminate at the midline but Nab2 mutant axons project to the contralateral side (white arrows). Insets show a magnified regions of the midline in each genotype. Control genotype: hsFLP/+;FRTG13,UAS-CD8-GFP/FRTG13, tubulin-GAL80;dNab2pex41/dNab2pex41;OK107-Gal4/+. Mutant genotype: hsFLP/+; FRTG13,UAS-CD8-GFP/FRTG13,tubulin-GAL80;dNab2ex3/dNab2ex3;OK107-Gal4/+.