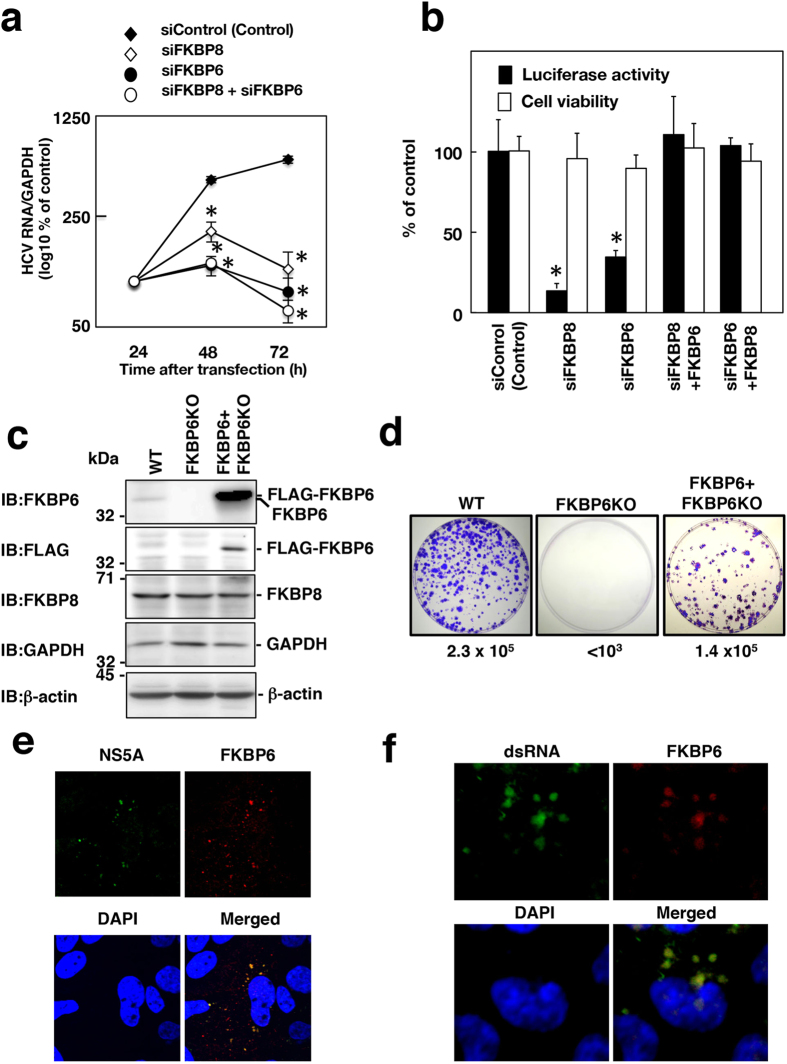
Figure 2. Effects of FKBP6 knockdown on HCV replication.
(a) Huh7OK1 cells infected with HCVcc (JFH-1) were transfected with siFKBP8 and/or siFKBP6 at 10 nM. Culture supernatants were harvested from HCVcc-infected cells at the indicated times after transfection with 10 nM siRNAs. Viral RNA was estimated by qRT-PCR, normalized with the value of GAPDH mRNA and is presented as a percent of the control. (b) Replicon O cells were transfected with siFKBP6 or siFKBP8 at a final concentration of 10 nM and incubated for 16 h. The resulting cells were transfected again with an empty plasmid or a plasmid encoding FKBP8 or FKBP6, further incubated for 56 h and then harvested in order to measure luciferase activity and cell viability. The values obtained were standardized to those of the control cells. The amount of total transfected siRNA was adjusted with siControl in the absence of one of the siRNAs targeting FKBPs. Asterisks indicate a significant difference versus the control value (*P < 0.05). The data shown in this figure are representative of three independent experiments. (c) Cell lysates were prepared from Huh7OK1 cells (WT), FKBP6KO cells and FKBP6KO Huh7OK1 cells expressing FLAG-FKBP6 (FKBP6 + FKBP6KO), and were subjected to immunoblotting. (d) A colony formation assay was performed. Colony formation efficiency (colony number per μg of transfected subgenomic RNA) is shown under each panel. (e) Endogenous FKBP6 and NS5A in the infected cells were stained with the first antibodies and the secondary fluorescent antibodies, and observed under a confocal microscope at 400 times magnification. (f) Endogenous FKBP6 and double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) in the infected cells were stained with a goat anti-FKBP6 antibody and mouse anti-dsRNA antibody, followed by staining with an AF594-conjugated donkey antibody to goat IgG and an AF488-conjugated goat antibody to mouse IgG, respectively. The secondary antibody to goat IgG was reacted first in order to avoid a cross-reaction. The localization of the stained proteins was analyzed by confocal laser scanning microscopy. The stained samples were observed under a confocal microscope at 600 times magnification.