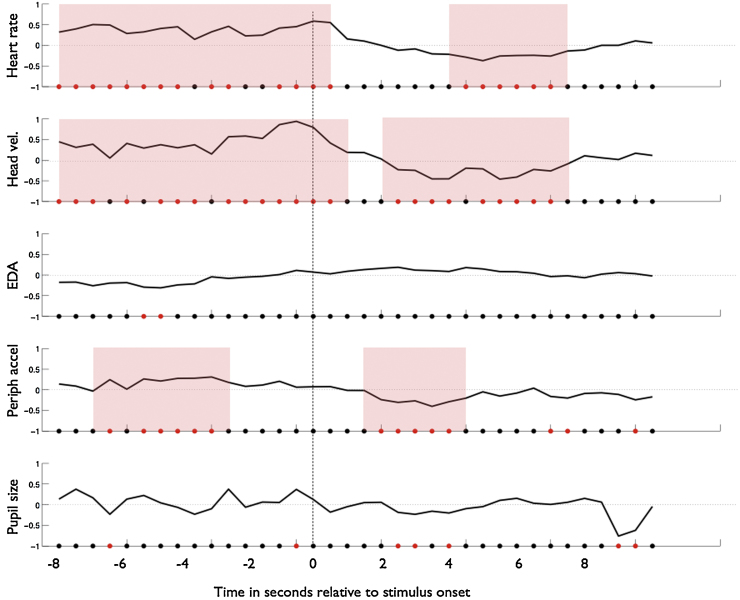
Fig. 7.
Arousal changes relative to stimulus onset. Plots show average z-score data obtained across all participants showing changes observed relative to the onset of a new stimulus. One-sample t-tests were conducted, epoch-by-epoch, to assess whether the average z scores obtained for that epoch and for that measure differ significantly from zero. A red dot on the x-axis indicates that, for that epoch, the average z scores obtained across all participants differ significantly from zero (p < .05). A black dot indicates that results obtained for that epoch do not differ significantly from zero. Phases that show a sustained period (more than two consecutive epochs) of significant difference from zero are marked with shaded pink areas. It can be seen that three measures – heart rate, head velocity and peripheral accelerometry – show periods of elevated activity prior to stimulus change and reduced activity post stimulus change. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)