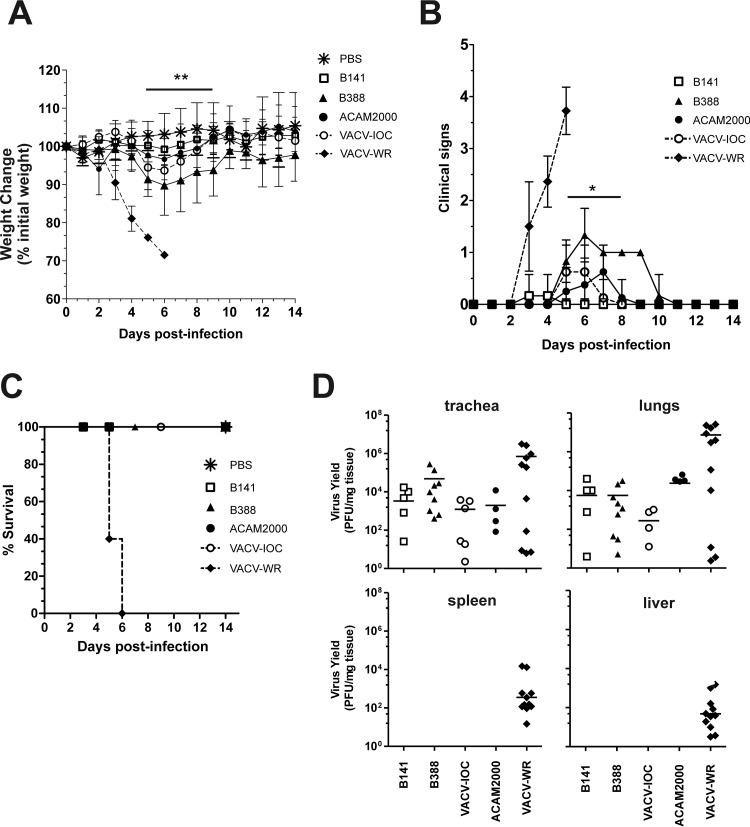
FIG 6.
Low virulence of B141 and B388 in murine intranasal infection model. BALB/c mice were infected intranasally with 1 × 107 PFU of B141, B388, VACV-IOC, or ACAM2000 or 5 × 105 PFU of VACV-WR. Weight changes (A), clinical signs (B), and survival (C) were monitored daily for 14 days. (A) Symbols represent the mean weight percentage (±SD) relative to day zero postinfection in 2 independent experiments (n = 4 mice per group per experiment). (B) Data points represent mean scores, and error bars represent ±SD. Mock-infected animals (PBS) did not show any clinical signs, and symbols were omitted for the sake of clarity. In panels A and B, horizontal bars above the symbols indicate the time points in which differences between B141- and B388-infected mice were statistically significant. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01 (one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's posttest). (D) Virus replication in primary and secondary sites of infection. Mice were euthanized 3 days postinfection when trachea, lungs, spleen, and liver were removed for virus titration as described in Materials and Methods. Each data point represents the virus titer of individual mice normalized by tissue protein concentration. Bars represent mean virus titers from 2 independent experiments (n = 5 mice per group per experiment).