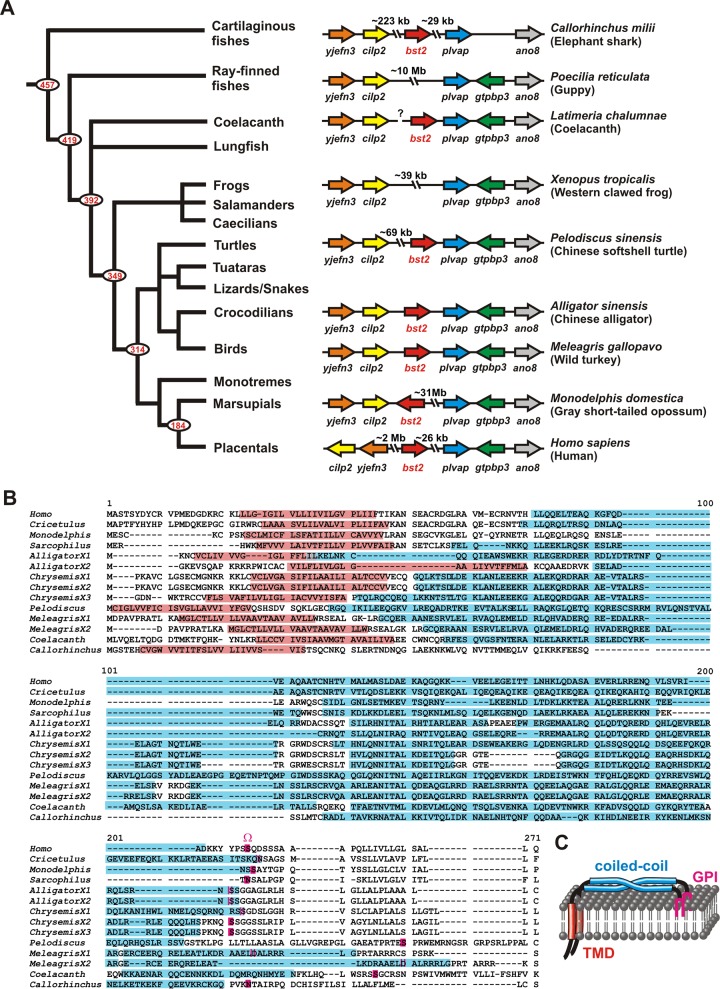
FIG 1.
Identification of previously undescribed tetherin orthologs. (A) Syntenic blocks containing yjefn3 (YjeF N-terminal domain-containing 3), cilp2 (Cartilage Intermediate-Layer Protein 2), bst2/tetherin, plvap (plasmalemma vesicle-associated protein), and ano8 (anoctamin 8) of diverse vertebrate species are shown on the right. Arrows indicate the direction of the ORFs. Gaps represent larger genome regions containing additional ORFs. A phylogenetic tree of vertebrate evolution (72) is shown on the left. Red numbers indicate divergence time estimates (in millions of years ago) for major nodes that are based on Inoue et al. (42). (B) Protein sequence alignment of tetherin orthologs from mammals, reptiles, and fishes. Dashes indicate gaps that were introduced to improve the alignment. Predicted TMDs are highlighted in red and coiled-coil regions in blue. The GPI anchor attachment site (Ω site) is shown in pink. X1 to X3 designate different tetherin isoforms from one species. (C) Cartoon of tetherin illustrating its typical topology comprising an N-terminal TMD (red), an extracellular coiled-coil domain (blue), and a C-terminal GPI lipid raft anchor (pink).