FIG 8.
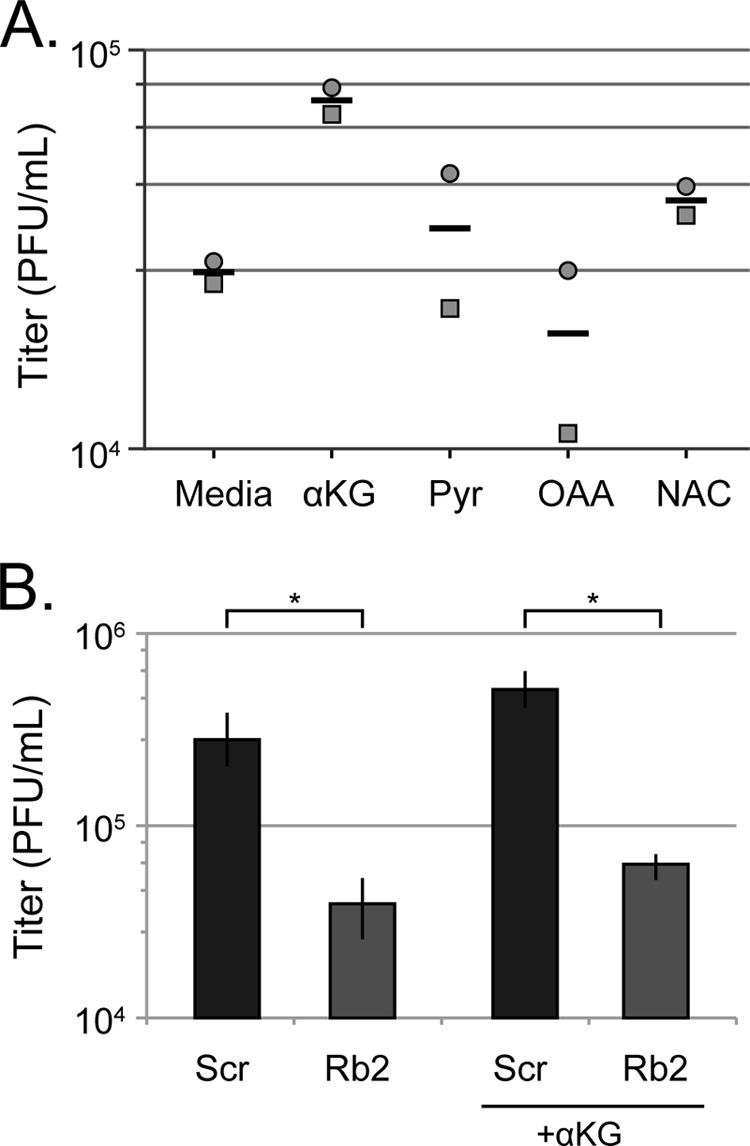
Rb knockdown cells produce sufficient citric acid cycle intermediates and antioxidants to support efficient HCMV replication (A) Serum-starved Rb knockdown cells were infected at an MOI of 1, and the medium was supplemented with α-ketoglutarate (α-KG), pyruvate (Pyr), oxaloacetic acid (OAA), or the antioxidant N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) at the time of infection and replenished at 48 h postinfection. Combined cell-free and cell-associated virus was collected 4 days postinfection, and the titers of virus were determined by standard plaque assay. The symbols represent individual experiments and horizontal bars are the mean from two experiments. (B) Serum-starved scrambled control (Scr) and Rb knockdown cells were infected at an MOI of 1 and left in normal medium or supplemented with α-KG, as in panel A. Combined cell-free and cell-associated virus was collected at 4 days postinfection, and the titers of virus were determined by standard plaque assay. The data are mean titers ± the standard deviations from six biological replicates. Statistical significance was determined by using the Student t test (*, P < 0.001). A Sen-Adichie test for parallelism determined there was no significant difference between the α-KG mediated increase in virus titers in the scrambled control and Rb knockdown cells (P > 0.3).
