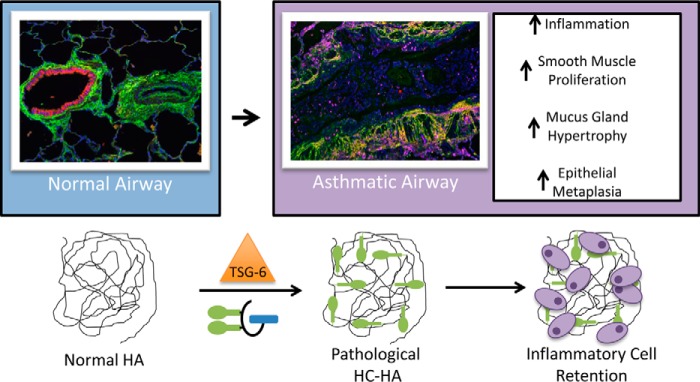
FIGURE 9.
Model for the role of the pathological heavy chain modification of hyaluronan in asthma. Under normal conditions, HA is present in the submucosa of airways and pulmonary vasculature as a very large, linear, glycosaminoglycan of the extracellular matrix, lacking any protein modifications. During asthma, the enzyme TSG-6 covalently transfers HCs from IαI to HA in the airway submucosa, forming the pathological HC-HA matrix. This structure promotes inflammatory cell adhesion and retention in the submucosa region of asthmatic airways. It may also influence smooth muscle cell proliferation, mucus gland hypertrophy, and epithelial metaplasia, leading to airway obstruction by the excessive production of mucus.