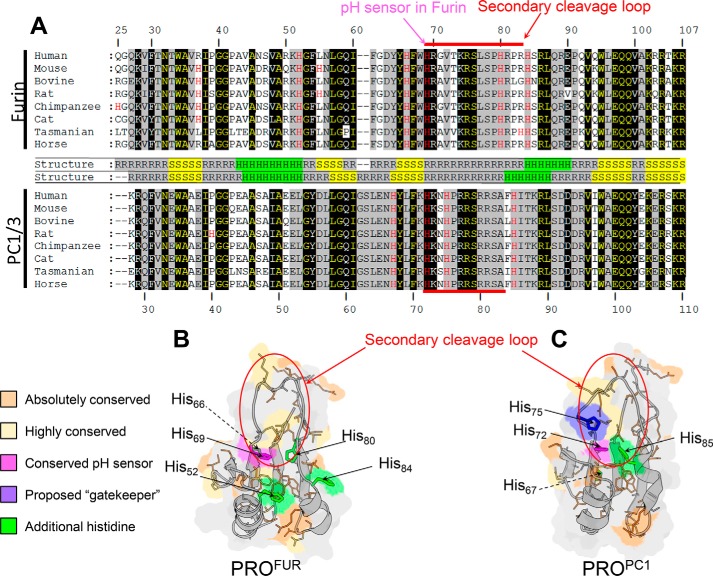
FIGURE 2.
Comparative analysis of PROFUR and PROPC1/3. A, multiple sequence alignment of eight orthologues of PROFUR (top) and PROPC1/3. Names of the species are denoted on the figure, and their corresponding accession numbers for furin are as follows: human, P09958; mouse, P23188; bovine, Q28193; rat, P23377; chimpanzee, H2QA34; cat, M3W594; Tasmanian devil, G3W614; and horse, F7DHR9. Similarly, the species and their corresponding accession numbers for PC1/3 are as follows: human: P29120; mouse: P63239; bovine, Q9GLR1; rat, P28840; chimpanzee, H2QR92; cat, M3W5Q0; Tasmanian devil, G3VJH4; and horse, F6TCF0. Residues are numbered with respect to the human homologue of each peptide. Residues that are absolutely conserved in orthologues of either PROFUR or PROPC1/3 are shaded in black, whereas those residues conserved in orthologues of both PROFUR and PROPC1/3 are in yellow text with black shading. Highly conserved residues are shaded in gray. Histidine residues are highlighted in red text with the conserved pH sensor indicated by the magenta arrow. Residues comprising the secondary cleavage loop are indicated by the red bar. In between sequence alignments, secondary structures are indicated: R indicates random coil, S indicates β sheet, and H indicates α helix. B, homology model for PROFUR (32). C, solution structure (Protein Data Bank code 1KN6) of PROPC1/3. The absolutely conserved residues in B and C are colored orange, and highly conserved residues are colored yellow. The conserved pH-sensing histidines in PROFUR and PROPC1/3 are colored magenta, and additional histidines are colored green with the proposed gatekeeper histidine residue in PROPC1/3 is colored purple. The secondary cleavage loop is circled in red.