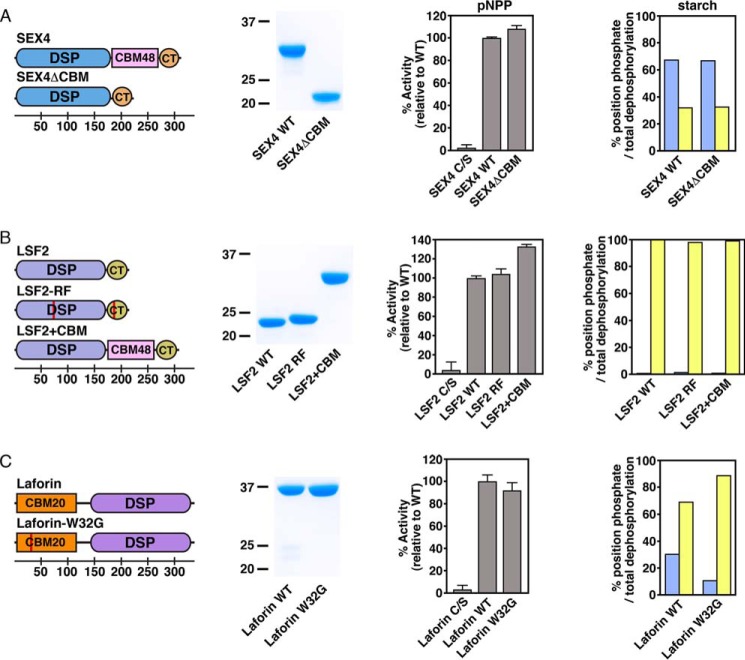
FIGURE 3.
Ancillary glucan binding domains in glucan phosphatase position-specific activity of A) SEX4, B) LSF2, and C) Laforin. Domain organization of glucan phosphatase constructs used in this study, including SEX4ΔCBM, LSF2-RF, LSF2+CBM, and laforin-W32G (first column). Red lines represent point mutations. Bottom scale represents residue number. Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE gel showing purified wild-type and variants (second column). Activity of glucan phosphatases and variants against para-nitrophenyl phosphate (pNPP) represented as percent activity relative to the wild type construct (third column). Error bars represent the ± S.D. of five replicates. Relative specific activity of wild type glucan phosphatases and variants at the C6 (blue) and C3 (yellow) positions of radiolabeled Arabidopsis starch represented as the percentage of total position dephosphorylation relative to total dephosphorylation (fourth column). Statistical analysis of wild type and mutant activities demonstrated no statistically significant differences, except for laforin wild type and laforin-W32G (p < 0.005).