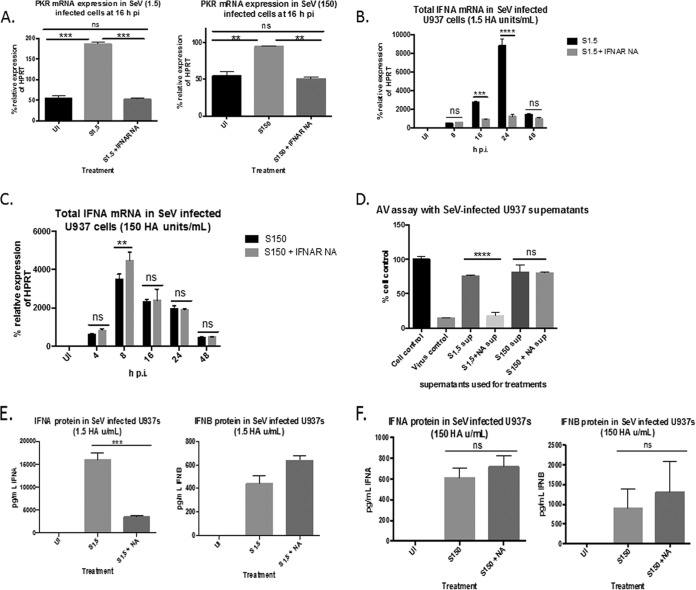
FIG 4.
Total IFN-α mRNA and protein induction is more reliant on IFNAR2 signaling in cells infected with 1.5 HA U/ml of SeV than in cells infected with 150 HA U/ml. (A) qRT-PCR analysis of PKR gene expression in cells infected with either 1.5 or 150 HA U/ml of SeV in the presence or absence of IFNAR2-neutralizing antibody. (B and C) Total IFN-α mRNA in cells infected with either 1.5 (B) or 150 (C) HA U/ml of SeV in the presence or absence of IFNAR-neutralizing antibody (NA). (D) Supernatants (sup) from cells infected with either 1.5 or 150 HA U/ml of SeV in the presence or absence of IFNAR NA (NA) for 24 h were used to pretreat fresh U937 cells in an antiviral assay using EMCV as the challenge virus. Cell viability was measured 72 h post-EMCV infection. Cell control, no pretreatment or infection; virus control, EMCV infected, no pretreatment. (E and F) ELISA measuring IFN-α protein (left) and IFN-β protein (right) in supernatants from cells infected with 1.5 (E) or 150 (F) HA U/ml of SeV in the presence or absence of IFNAR2 NA. Statistics were performed using a two-way ANOVA (B and C) and one-way ANOVA (A and D to F). Bonferroni posttest analyses were performed. **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001; ns, not significant. The data are representative of 3 biological replicates performed in duplicate. qRT-PCR data are shown as the percent relative expression of HPRT. The error bars indicate the standard error of the mean.