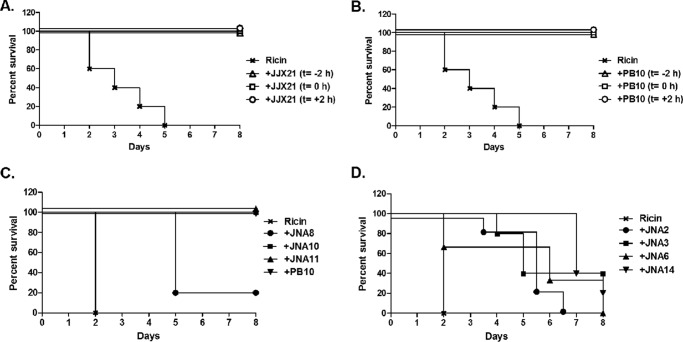
FIGURE 1.
Neutralization of ricin toxin by VHH heterodimers and homodimers in a mouse model. A, VHH heterodimer JJX21, and B, mAb PB10 were each administered to adult BALB/c mice (n = 5 mice per group) 2 h prior (t = −2 h), concurrent with (t = 0), or 2 h after (t = +2 h) a 10× LD50 of ricin challenge. Survival was monitored for 8 days. C, VHH heterodimers (JNA8, JNA10, and JNA11), or D, VHH homodimers (JNA2, JNA3, JNA6, and JNA14) were mixed with 10× LD50 of ricin at an 8:1 molar VHH:toxin ratio, and then injected intraperitoneally into BALB/c mice (n = 5 mice per group). Survival was monitored for a total of 8 days. Antibody PB10 was used as a positive control for these studies, as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Panels A and B correspond to a single experiment with shared controls, but were separated for clarity. It should be noted that VHH constructs JNA8, JNA2, JNA3, JNA6, and JNA14 significantly extend time to death, as compared with toxin-only treated mice (p < 0.05; Log-Rank Mantel-Cox test).