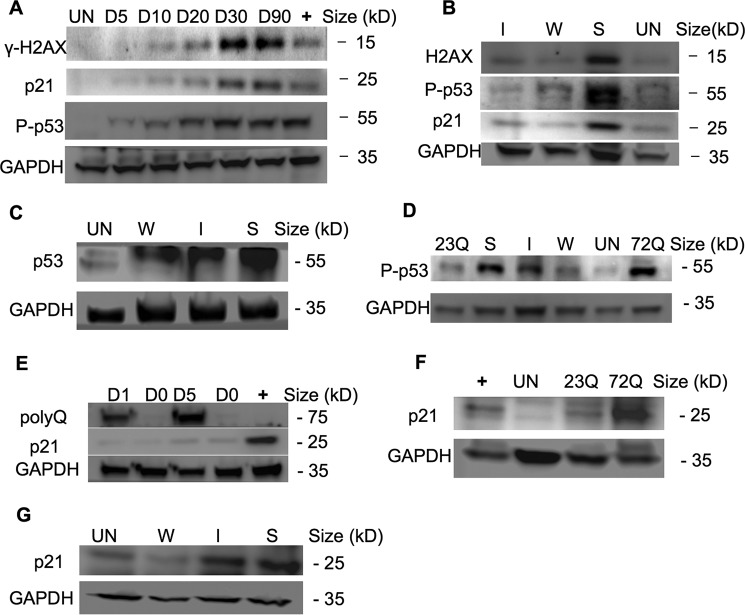
FIGURE 3.
p53 activates the DNA damage checkpoint in aggresome-containing cells, leading to mitotic arrest. A, γ-H2AX, P-p53 (Ser-15), and p21 were gradually elevated in EGFP-HDQ72 cells over a 3-month expression period. Bar charts show the quantification of γ-H2AX, P-p53, and p21 normalized against GAPDH. Positive control: long term-induced EGFP-HDQ23 cells treated with hydroxyurea (1.5 mm) for 8 h to activate P-p53. Un, uninduced cells. B, immunoblotting showed P-p53 (Ser-15) and p21 are correlated with polyQ expression level, which increases with polyQ expression driven by weak (W), intermediate-strength (I), or strong (S) promoters. Bar charts show the quantification of γ-H2AX, P-p53 (Ser-15), and p21 normalized against GAPDH. C, overall p53 level was significantly elevated in cells in which SNAP-HDQ72 expression was driven by a strong promoter over a 3-month period. Uninduced EGFP-HDQ23 cells were used as the negative control. D, P-p53 (Ser-15) was significantly elevated in cells in which EGFP-HDQ72 and SNAP-HDQ72 expression was driven by a strong promoter over a 3-month period. E, expression of p21 lagged behind polyQ expression. The positive control was uninduced EGFP-HDQ23 cells treated with hydroxyurea (1.5 mm) for 8 h. F, p21 levels were significantly elevated in long term-induced EGFP-HDQ72 cells while remaining low level in uninduced and EGFP-HDQ23 cells. The positive control was long term-induced EGFP-HDQ23 cells treated with hydroxyurea (1.5 mm) for 8 h. G, immunoblotting showed p21 levels were correlated with polyQ expression level. SNAP-HDQ72 expression was driven by weak (W), intermediate-strength (I), or strong (S) promoters.