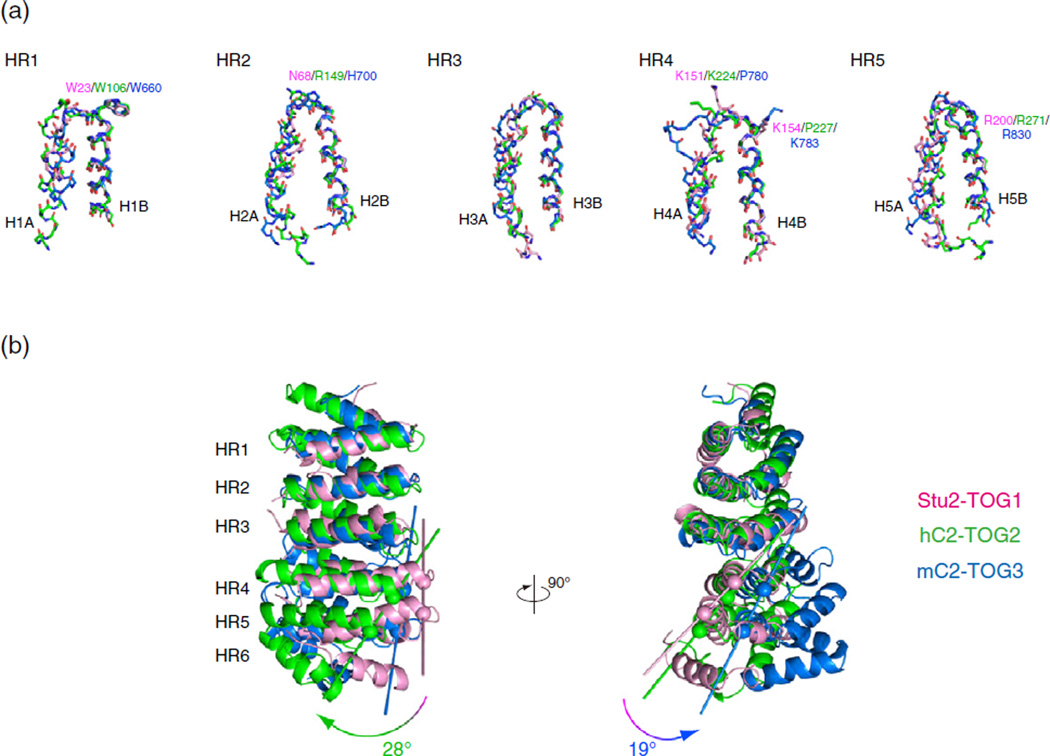
Fig. 4.
Dissection of the TOG domains. (a) Structural alignment of HRs. Structures of HR1-5 from hC2-TOG2 (green), mC2-TOG3 (blue) and Stu2-TOG1 (pink) are superimposed using the main-chain Cα atoms of 15 residues in the B helix of each HR. The secondary structure is defined using DSSP [53]. The side chains of the residues involved in tubulin recognition are shown and labeled. (b) Superposition of hC2-TOG2 (green), mC2-TOG3 (blue) and Stu2-TOG1 (pink). Structures are superimposed using the B helices of HR1-3. The curvature was defined as the angle between two vectors connecting the N-terminal Cα atoms of H4B and H5B. The Cα atoms used for creating these vectors are indicated with spheres.