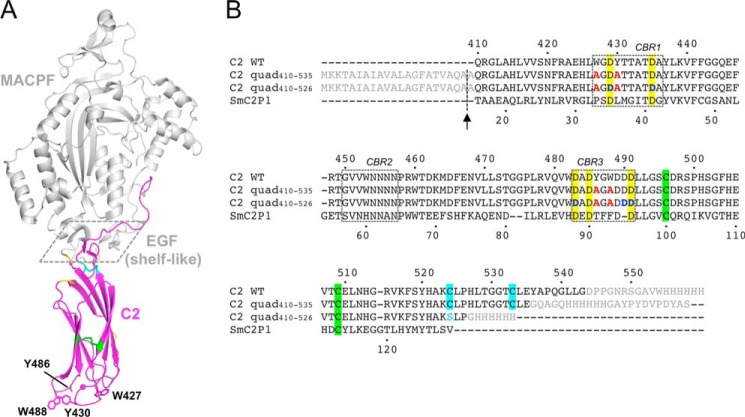
FIGURE 1.
Crystal structure of murine perforin. A, crystal structure of murine perforin, PDB code 3NSJ (7), is shown with the C2 domain colored in magenta. The hydrophobic aromatic residues (Trp-427, Tyr-430, Tyr-486, and Trp-488) are shown in a stick representation where the side chain density of Tyr-486 is disordered. Two Ca2+ ions are indicated as magenta spheres. The MACPF and EGF domains are shown in gray. The shelf-like region is boxed with dashed line. Disulfide bonds between Cys-496 and Cys-509, and between Cys-524 and Cys-535 are represented by green and cyan sticks, respectively. The residues (410, 411, 461, 471, and 472), whose resonances were undetected in the current NMR study, are shown in yellow. B, sequence alignment of mouse perforin (Prf) C2 and the C2 quad mutant constructs used in the analyses carried out in this study. Amino acid sequences of the mouse perforin C2 domain (C2 WT) and the C2 quad mutants used for the current crystal (C2 quad(410–535)) and NMR studies (C2 quad(410–526)) together with SmC2P1 are aligned. The N-terminal signal sequence and the C-terminal additional sequences, including the hemagglutinin (HA) and/or His6 tag, are shown in gray. The four alanine residues substituted from the WT aromatic residues are illustrated in red. Five conserved Asp residues are highlighted in yellow. The positions of Asp-Asn mutations (Asp-429, Asp-435, Asp-483, Asp-490, and Asp-491) are colored in blue. Sequence numbers of the mouse perforin C2 domain and SmC2P1 are shown above and below the primary sequences, respectively. The positions of the CBRs are boxed. The signal sequence was cleaved during the export process at the position indicated by the arrow, resulting in an alanine overhang at the N terminus. Pairs of Cys residues that form disulfide bonds are highlighted in the same colors as in A. In the C2 quad(410–526), Cys-524 was mutated to serine (cyan) to remove a free thiol in the construct.