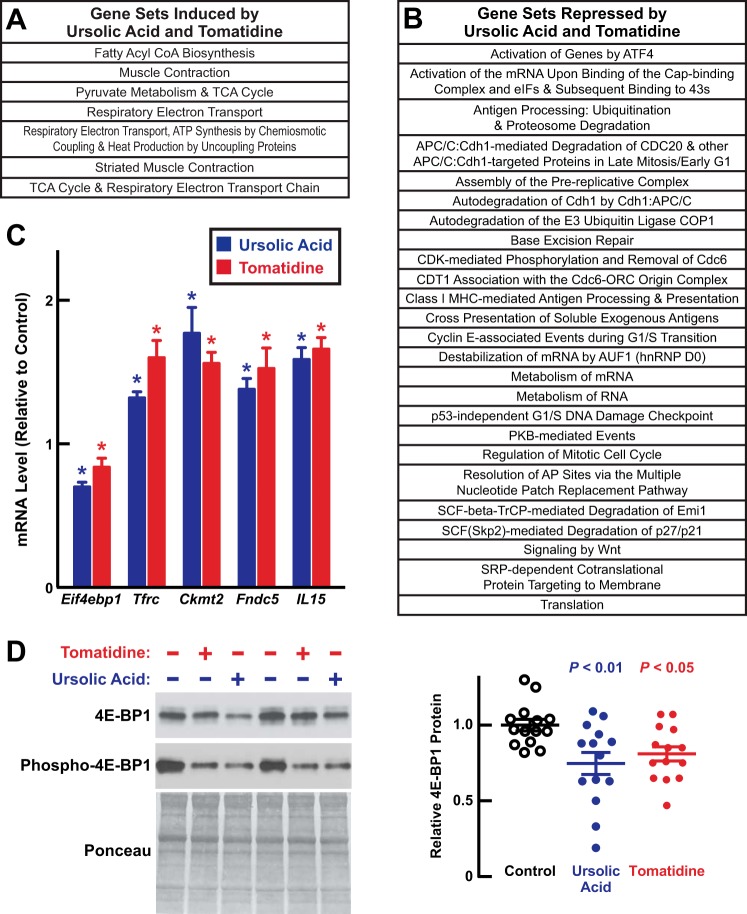
FIGURE 6.
Ursolic acid and tomatidine significantly induce or repress numerous gene sets in aged skeletal muscle, including repression of the gene set activation of genes by ATF4. A and B, array data from Fig. 5 were subjected to gene set enrichment analysis. Statistical significance was defined as p < 0.05 and FDR < 0.25. A, reactome gene sets that were significantly induced in the quadriceps of both ursolic acid-treated mice and tomatidine-treated mice relative to control mice. B, reactome gene sets that were significantly repressed in the quadriceps of both ursolic acid-treated mice and tomatidine-treated mice relative to control mice. C and D, data are from quadriceps muscles of 22-month-old C57BL/6 mice in Fig. 2 that were treated for 2 months with control diet, ursolic acid diet, or tomatidine diet. C, levels of the indicated transcripts were assessed with qPCR. Data are means ± S.E. from five mice per condition. D, quadriceps protein extracts were subjected to immunoblot analysis with anti-4E-BP1 or anti-phospho-4E-BP1 antibodies. Left, representative immunoblots. Membranes were stained with Ponceau S to confirm equal loading. Right, quantification of total 4E-BP1. Each data point represents one mouse, and horizontal bars denote means ± S.E. In C and D, p values were determined with a one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's multiple comparison test. *, p ≤ 0.05. TCA, tricarboxylic acid; hnRNP, heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein; CDK, cyclin-dependent kinase; APC/C, anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome; SRP, signal recognition particle; ORC, origin recognition complex; AP, apurinic/apyrimidinic.