FIGURE 5.
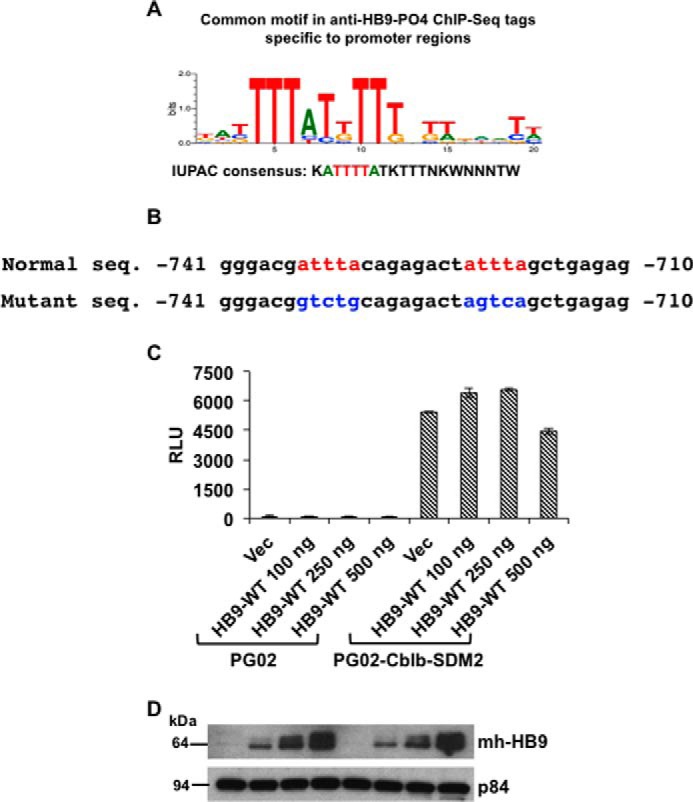
HLXB9 binding motif in the Cblb promoter. A, consensus motif in anti-HB9-PO4 ChIP-Seq tags located at promoter regions. De novo motif analysis from anti-HB9-PO4 ChIP-Seq tag sequences located at promoter regions was performed using Genomatix software. A core sequence ATTTTA was identified that resembles homeodomain-binding consensus (35). B, sequence of the HLXB9 binding motifs in the Cblb promoter. The top line shows the putative HLXB9 binding motifs (red) in the DNA sequence of the Cblb promoter (−741 to −710 region from the transcriptional start site is shown). The bottom line shows nucleotide substitutions (blue) to mutate the motifs by site-directed mutagenesis in the Cblb-promoter construct used in C. C and D, HLXB9 did not suppress the activity of the Cblb promoter containing mutations at the HLXB9 binding motifs. The putative HLXB9 binding motifs shown in B were mutated by site-directed mutagenesis of the PG02-Cblb promoter construct and analyzed for promoter activity in MIN6-4N cells. RLU for each of the transfections are shown. Compared with the empty vector PG02, the PG02-Cblb-SDM2 plasmid showed significantly high RLU and co-expression of increasing amounts of HLXB9 did not suppress the Cblb promoter activity. Error bar = Mean and S.D. from 3 experiments, * = p < 0.05. A representative Western blot shows expression of HLXB9 (with anti-myc-tag) in the MIN6-4N cells analyzed for luciferase activity. p84 was used as the loading control.
