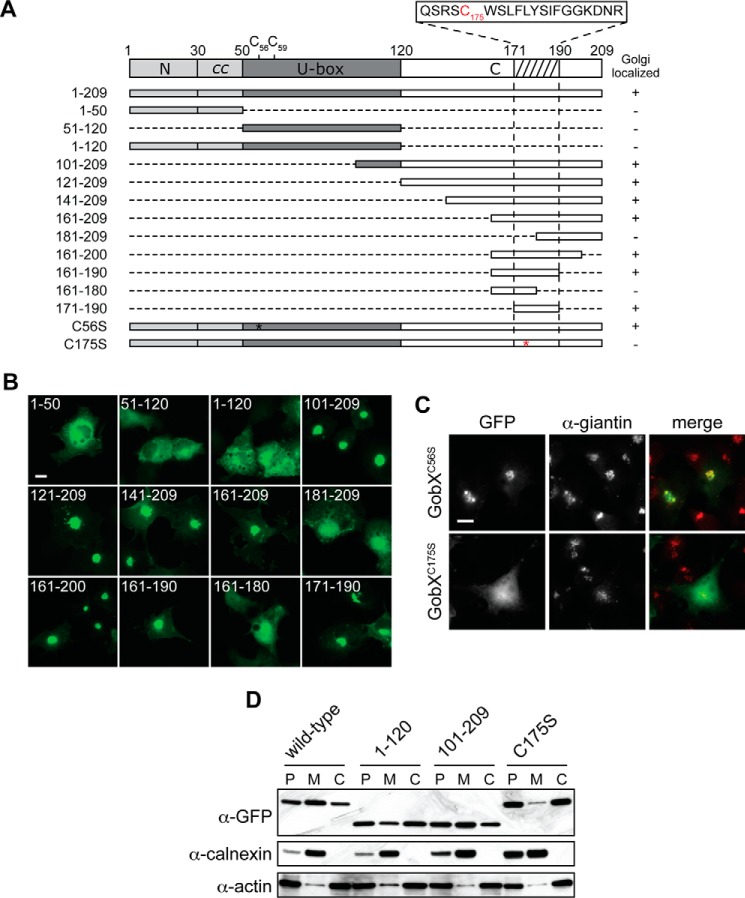
FIGURE 4.
Cys-175 is required for the Golgi localization of GobX. A, schematic illustration of the GobX variants. Dashed lines indicate regions deleted in the truncated GobX variants. The asterisk denotes the position of cysteine to serine substitution in GobX. The minimal Golgi-localizing fragment (residue 171–190) is indicated by the hatched box, and the amino acid sequence of this region is shown with Cys-175 highlighted in red. The other two cysteine residues located within the U-box domain (Cys-56 and Cys-59) are also shown. Asterisk, position of C175S substitution in GobX. GobX variants that localize to the Golgi region (as shown in B and C are marked with +, and variants that showed cytosolic distribution are marked −. B, 20-amino acid region is sufficient to target GobX to the Golgi region. The GobX variants described in A were produced as GFP fusions in transiently transfected COS-1 cells and analyzed for their subcellular distribution. Scale bar, 2 μm. C, subcellular localization of GobX is affected by C175S substitution. The GFP-GobX mutants C56S and C175S were produced in transiently transfected COS-1 cells. Cells were chemically fixed and labeled with anti-giantin antibody. Scale bar, 2 μm. D, HEK293T cells producing wild-type GFP-GobX or the indicated GobX variants were homogenized. The post-nuclear (P) supernatant was subsequently fractionated into the membrane (M) and cytosolic (C) fraction. The presence of GobX in each fraction was detected by immunoblot using anti-GFP antibody. Calnexin and actin served as markers for the membrane and cytosolic fraction, respectively. All immunofluorescence images and immunoblots are representatives of at least two independent experiments with similar outcomes.