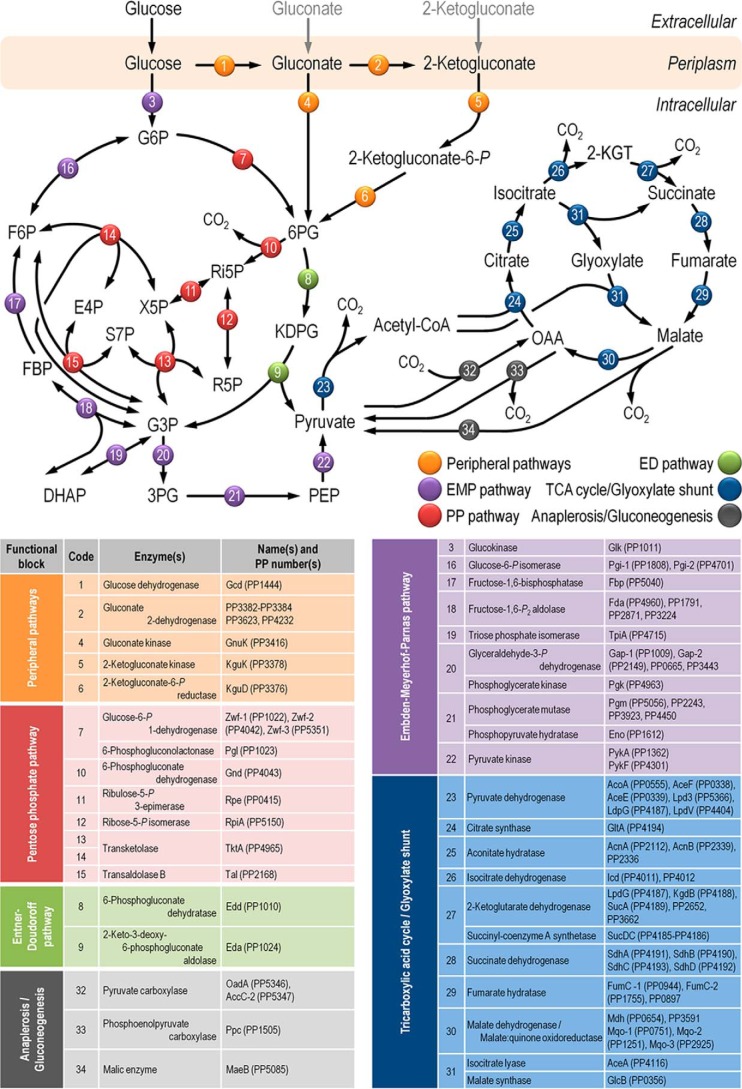
FIGURE 1.
Biochemical pathways involved in glucose catabolism in P. putida KT2440. The transformations that take place in the outer membrane and in the periplasmic space are shown at the top of the scheme, along with the transport of glucose, gluconate, and 2-ketogluconate into the cell cytoplasm. The metabolic network was sketched around six main metabolic blocks, identified with different colors: (i) the peripheral pathways, that encompass the oxidative transformation of glucose into gluconate and 2-ketogluconate (and the corresponding phosphorylated derivatives of these metabolites); (ii) EMP pathway (non-functional, due to the absence of a 6-phosphofructo-1-kinase activity); (iii) the pentose phosphate (PP) pathway; (iv) the ED pathway; (v) the tricarboxylic acid cycle and glyoxylate shunt; and (vi) anaplerotic and gluconeogenic bioreactions. Some bioreactions have been lumped to simplify the diagram. The transport of gluconate and 2-ketogluconate from the extracellular space is indicated by gray arrows. The complete list of the enzymes and isozymes catalyzing each reaction is shown below the biochemical network. The information for the network was compiled from the Pseudomonas Genome Database (75) and MetaCyc (76) and several studies available in the literature (3, 5, 7, 8, 11). In the instances in which no gene name has been assigned, the PP number is given for each open reading frame. Note that, according to Nelson et al. (77), pckA (encoding phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase) contains an authentic frameshift and therefore the open reading frame is classified as a pseudogene in the Pseudomonas Genome Database (75). Abbreviations are as follows: G6P, glucose-6-P; F6P, fructose-6-P; FBP, fructose-1,6-P2; DHAP, dihydroxyacetone-P; 6PG, 6-phosphogluconate; KDPG, 2-keto-3-deoxy-6-phosphogluconate; Ri5P, ribulose-5-P; R5P, ribose-5-P; X5P, xylulose-5-P; S7P, sedoheptulose-7-P; E4P, erythrose-4-P; G3P, glyceraldehyde-3-P; 3PG, glycerate-3-P; PEP, phosphoenolpyruvate; Acetyl-CoA, acetyl-coenzyme A; OAA, oxaloacetate; 2-KGT, 2-ketoglutarate; and Pi, inorganic phosphate.