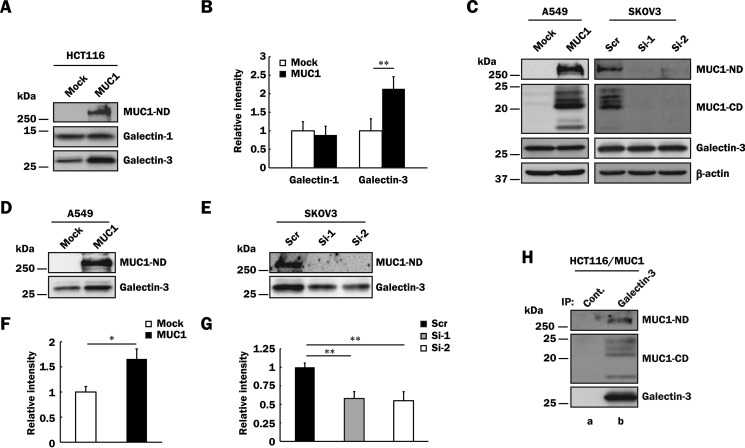
FIGURE 2.
Binding of galectin-3 to MUC1 in various MUC1-expressing cells. A, HCT116/Mock and HCT116/MUC1 cells were treated with biotin as described under “Experimental Procedures,” and the cell surface proteins were precipitated from the lysates with streptavidin-Sepharose. The precipitates were subjected to SDS-PAGE, followed by Western blotting and detection with anti-MUC1-ND, anti-galectin-1, and anti-galectin-3 antibodies. B, the levels of galectin-1 and -3 on the cell surface were determined by measuring the intensities of their bands in Fig. 2A with ImageJ. The respective intensities of galectin-1 and -3 in control cells were taken as 1 (means ± S.D., n = 3). **, p < 0.01. C, lysates of A549/Mock, A549/MUC1, SKOV3/Scr, SKOV3/Si-1, and SKOV3/Si-2 cells were subjected to SDS-PAGE, followed by Western blotting as described in Fig. 1C. β-Actin was used as a loading control. D and E, A549/Mock, A549/MUC1 (D), SKOV3/Scr, SKOV3/Si-1, and SKOV3/Si-2 (E) cells were labeled with biotin, and then MUC1-ND and galectin-3 on the cell surface were detected as described in Fig. 2A. F and G, the intensity of galectin-3 in Fig. 2 (D and E) was determined and normalized as described in Fig. 2B (means ± S.D., n = 3). *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01. H, galectin-3 was immunoprecipitated (IP) from lysates of HCT116/MUC1 cells with anti-galectin-3 antibodies (lane b) or control IgG (lane a) and then subjected to SDS-PAGE, followed by Western blotting and detection with anti-MUC1-ND, anti-MUC1-CD, and anti-galectin-3 antibodies.