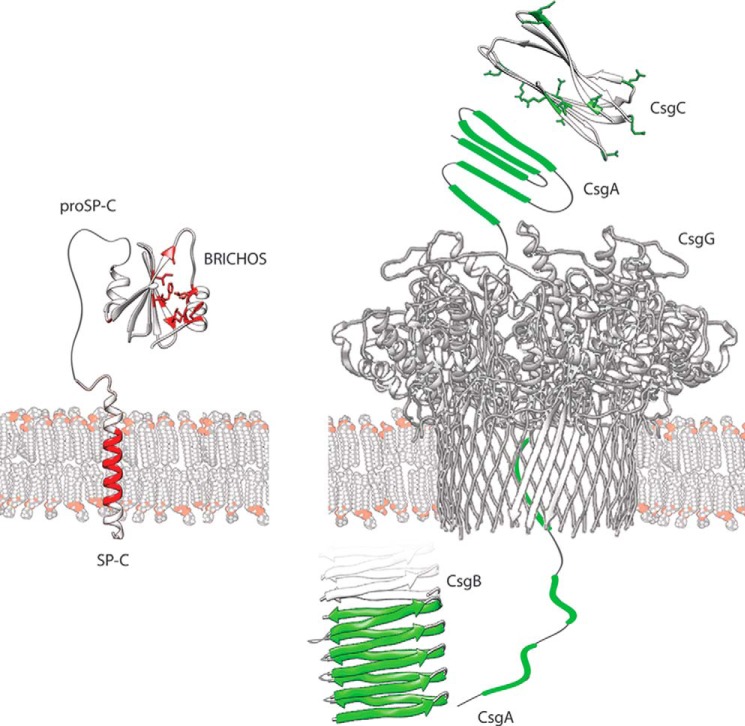
FIGURE 1.
Architectures of proSP-C and the bacterial curli system. Left side, ProSP-C is shown with its transmembrane SP-C part in red. The proSP-C BRICHOS domain, located in the endoplasmic reticulum lumen, prevents the aggregation of the amyloidogenic SP-C segment. Hydrophobic residues in the putative client-binding face A of the central β-sheet and its opposing helix 1 are highlighted in red. Right side, for the curli system, the amyloidogenic segments in CsgA and the Gln residues in CsgC are highlighted in green. CsgC keeps CsgA in a soluble state for export through the secretion channel CsgG. In the extracellular space, CsgB nucleates the assembly of CsgA into curli fibers.