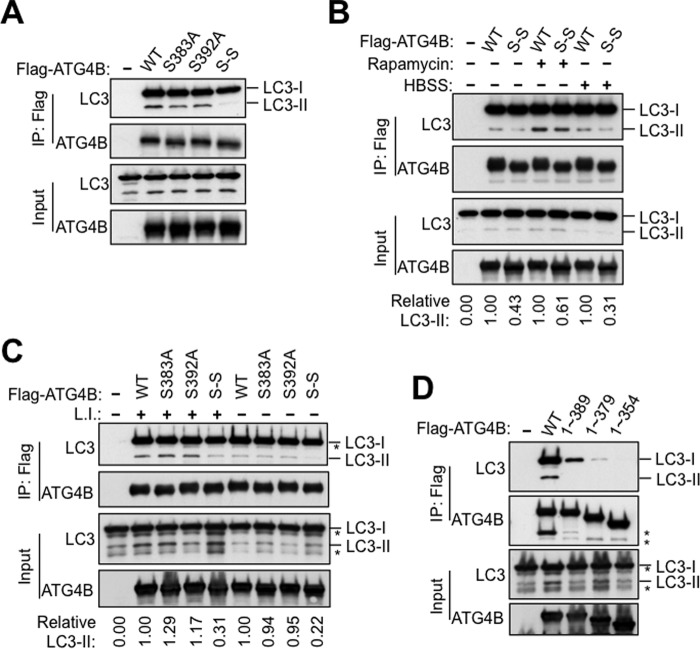
FIGURE 6.
Phosphorylation-deficient ATG4B mutants show impaired interaction with lipidated LC3. A–C, S383A and S392A mutations attenuate the interaction between ATG4B and PE-conjugated LC3 (LC3-II). Flag-ATG4B or S383A, S392A, S383A-S392A (S-S) mutants were co-transfected with GFP-LC3 for 48 h in HEK293T cells. After transfection, cells were treated with rapamycin or HBSS for 4 h in B, or with or without lysosomal inhibitors for 4 h in C. Cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-Flag M2 affinity gel. The IP complexes and cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting as indicated using anti-LC3, anti-ATG4B, and anti-GFP antibodies. In B and C, the relative amount of pulled-down LC3-II was quantified by scanning densitometry, normalized to the amount in the total lysate, and further normalized to ATG4B WT (values shown below lanes). D, C-terminal region of Atg4B is essential for cellular interaction with LC3. Plasmids encoding Flag-ATG4B full-length or various truncation mutants of ATG4B were co-transfected with GFP-LC3 into HEK293T cells. After 48 h, cell lysates were prepared, subjected to anti-Flag immunoprecipitation, and the immune-complexes were analyzed by immunoblotting as described above.