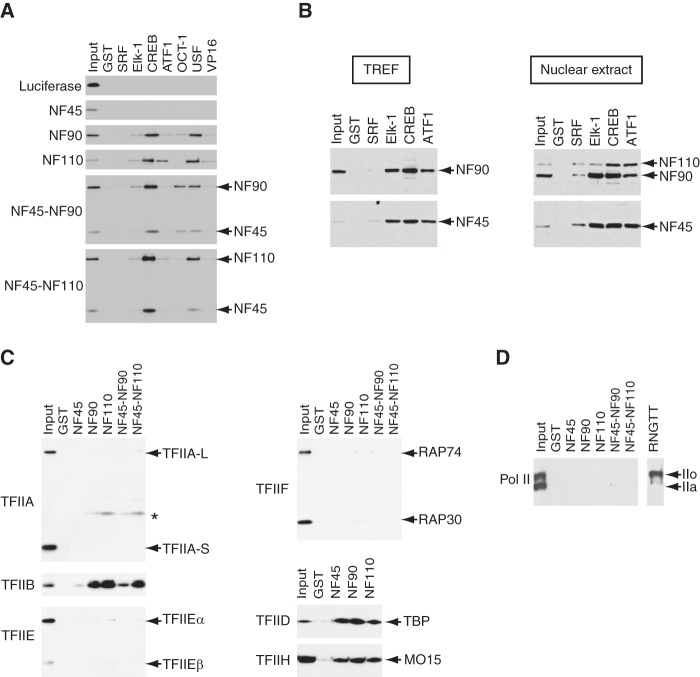
FIGURE 7.
The NF proteins interact with activators and the components of the basal transcriptional machinery. A, FLAG-tagged NF proteins or their complexes were tested for interactions with GST-fused activators retained on glutathione-Sepharose 4B. The bound proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and visualized by immunoblots using anti-FLAG antibody. B, the TREF fraction (2.24 mg) or HeLa nuclear extract (4.67 mg) was used in place of purified NF complexes for interaction assays as performed in A. Anti-NF90/NF110 or anti-NF45 antibody was used to detect the NF proteins in the bound proteins. The amounts of bound proteins were 2.1%, 1.9%, 1.9%, 2.3%, and 2.0% of the TREF fraction for GST, GST-SRF, GST-Elk-1, GST-CREB, and GST-ATF1, respectively. Similarly, the amounts of bound proteins were 1.5%, 1.2%, 1.3%, 1.1%, and 1.0% of HeLa nuclear extract for GST, GST-SRF, GST-Elk-1, GST-CREB, and GST-ATF1, respectively. C, FLAG-tagged general transcription factors were tested for interactions with GST-fused NF proteins. In TFIIH and TFIID, MO15 and TBP were tagged with FLAG. In the complexes of NF45-NF90 and NF45-NF110, NF45 was expressed as a GST fusion protein and heterodimerized in insect cells with NF90 and NF110, respectively. The asterisk indicates a nonspecific band. D, partially purified RNAPII from HeLa cells were tested for interactions with the NF proteins. IIo and IIa indicate the positions of hyperphosphorylated and unphosphorylated forms of RNAPII, respectively. RNGTT indicates RNA guanylyltransferase and 5′-phosphatase.