FIGURE 11.
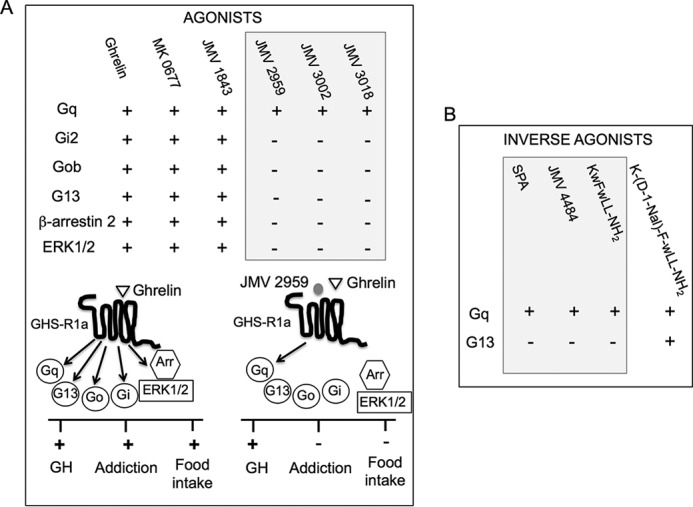
Outline of the functional selectivity of GHS-R1a ligands at GHS-R1a signaling. A, agonists. Ghrelin, MK-0677, and JMV 1843 are agonists (+) for all pathways, whereas JMV 2959, JMV 3002, and JMV 3018 compounds are partial agonists for Gq and neutral (−) toward the other pathways. Schematic drawings represent signaling pathways and in vivo effects promoted by ghrelin upon binding to GHS-R1a. Ghrelin, the endogenous ligand of GHS-R1a, activates Gq-, Go-, Gi-, and G13-dependent pathways and induces arrestin recruitment and ERK1/2 phosphorylation, resulting in GH secretion, food intake, and addiction. JMV 2959 antagonizes ghrelin action at Go, Gi, arrestin, and ERK but inhibits only partially Gq resulting in inhibition of addiction and food intake but not to inhibition of GH secretion. The possible connection between selectivity of JMV 2959 toward signaling pathways and physiological responses remains to be established. B, inverse agonists at Gq and G13. K-(D-1-Nal)-F-wLL-NH2 is an inverse agonist at both Gq and G13, whereas SPA, JMV 4484, and KwFwLL-NH2 are inverse agonists for both Gq and G13. Physiological consequences of the inverse agonism selectivity at Gq and G13 remain to be explored.
