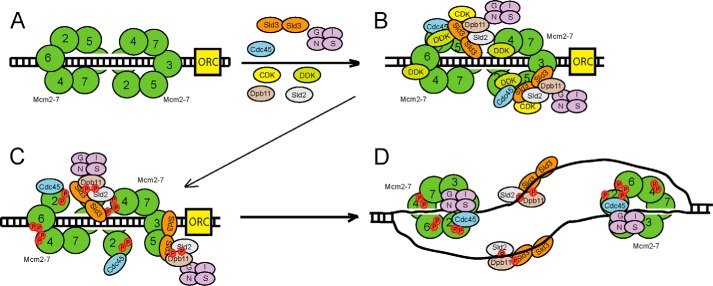
FIGURE 7.
Sld3 orchestrates the assembly of the replication fork helicase in budding yeast during S phase. A, the Mcm2–7 complex is loaded as a double hexamer in G1 phase by ORC, Cdc6 (not shown), and Cdt1 (not shown). B, two subunits of Sld3 form a tetramer with two subunits of Sld7 (not shown). DDK is recruited to Mcm2–7 during S phase. CDK is recruited to Sld2 and Sld3 during S phase. Sld3 recruits Cdc45 to Mcm2–7, and Sld3 also stimulates DDK phosphorylation of Mcm2. C, DDK phosphorylation of Mcm2–7 opens the Mcm2-Mcm5 gate, allowing for the extrusion of ssDNA from the central channel of Mcm2–7. D, once ssDNA is extruded from the central channel of Mcm2–7, the Sld3-Sld2-Dpb11 complex releases from Mcm2–7, and binds to ssDNA instead. This allows for the attachment of GINS to Mcm2–7 by a passive, sequestration mechanism. The interaction between Sld3 and ssDNA is required for the association of GINS with Mcm2–7. The helicase is now fully assembled.