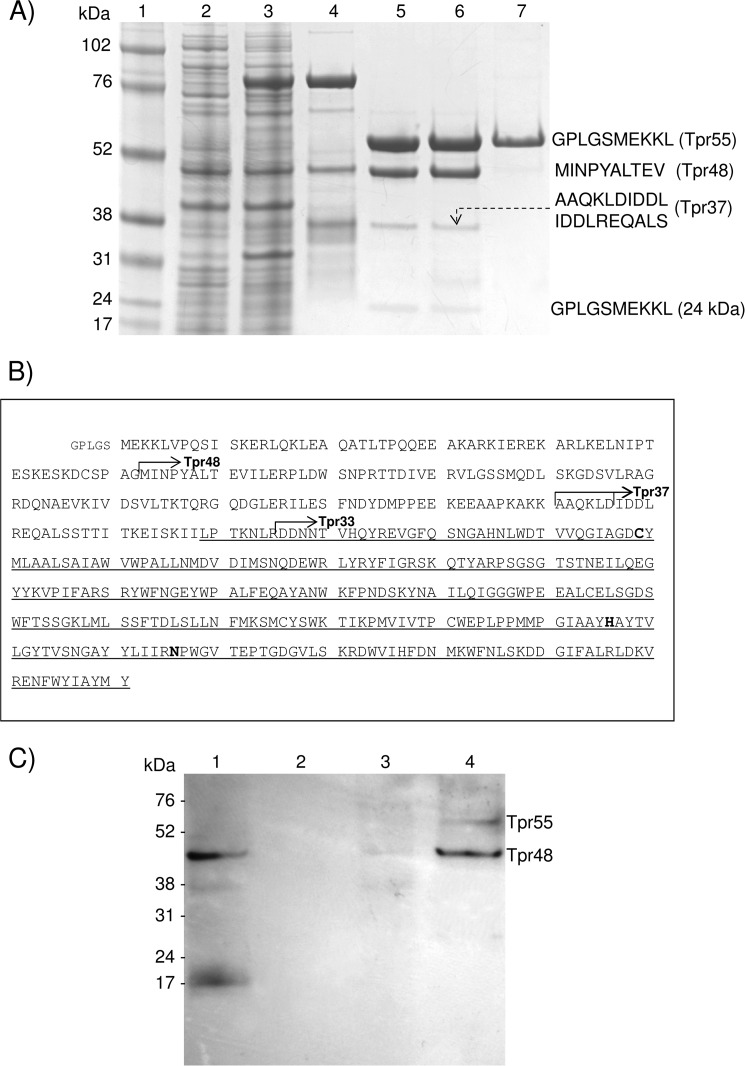
FIGURE 1.
Expression of WT and catalytic mutant Tpr and assessment of their autoprocessing activities. A, both WT (Tpr) and the active-site cysteine-to-serine mutant (TprC229S) were expressed in E. coli and purified. Lane 1, molecular mass marker (kDa); lanes 2 and 3, cell extracts of E. coli before and 3 h after induction of GST-Tpr expression with isopropyl-1-thio-β-d-galactopyranoside, respectively; lane 4, a fusion protein GST-Tpr (84 kDa) obtained from E. coli extract by affinity chromatography on glutathione-Sepharose; lane 5, Tpr55, Tpr48, and Tpr37 after GST was cleaved off by PreScission Protease and removed on glutathione-Sepharose; lane 6, Tpr55, Tpr48, and Tpr37 purified by gel filtration; lane 7, TprC229S (55 kDa) expressed and purified in the same way as WT Tpr. N-terminal sequences of Trp55, TprC229S, Tpr48, and Tpr37, determined by Edman degradation, are shown on the right side. B, the primary structure of Tpr with identified proteolytic cleavage sites (arrows) that generated the Tpr48 (Gly-62–Met-63), Tpr37 (Lys-160–Ala-161 and Asp-166–Ile-167), and Tpr33 (Arg-195–Asp-196) forms of the peptidase. Catalytic residues (Cys-229, His-406, and Asn-426), identified by alignment of the Tpr sequence with papain- and calpain-like peptidases, are in bold font. A domain similar to papain is indicated by a thin underline, starting from Leu-189. Of note, Tpr is encoded without a signal peptide. A pentapeptide (small font) preceding Met-1 is derived from the plasmid. C, Tpr55 and Tpr48 were localized in P. gingivalis W83 outer membrane and cellular extract. Lane 1, whole cellular extract; lane 2, cytoplasmic/periplasmic fraction; lane 3, inner membrane fraction; lane 4, sarkosyl-insoluble outer membrane fraction. Western blot analysis of cell fractions of P. gingivalis were probed with Tpr-specific rabbit antiserum.